Overview
The article provides a comprehensive overview of various sample revenue models, including subscription, freemium, transactional, advertising, and licensing models, and emphasizes their significance for businesses in generating income and ensuring sustainability. It supports this by illustrating how different companies successfully implement these models, such as Adobe's shift to subscription services and Dropbox's freemium approach, highlighting the importance of selecting the right model based on market trends, customer behavior, and strategic goals.
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of modern business, understanding revenue models is paramount for achieving sustainable growth and profitability. These frameworks dictate how companies generate income through their products and services, influencing everything from pricing strategies to market positioning.
As industries evolve, particularly in the technology sector, a well-defined revenue model can be the differentiator between thriving enterprises and those facing financial difficulties. By exploring various revenue models—such as subscription, freemium, and transactional—businesses can tailor their approaches to meet market demands and consumer preferences.
This article delves into the significance of revenue models, examines successful case studies, and provides key considerations for selecting the most effective strategy, all while highlighting the challenges that organizations must navigate in an ever-changing economic environment.
Understanding Revenue Models: Definition and Importance
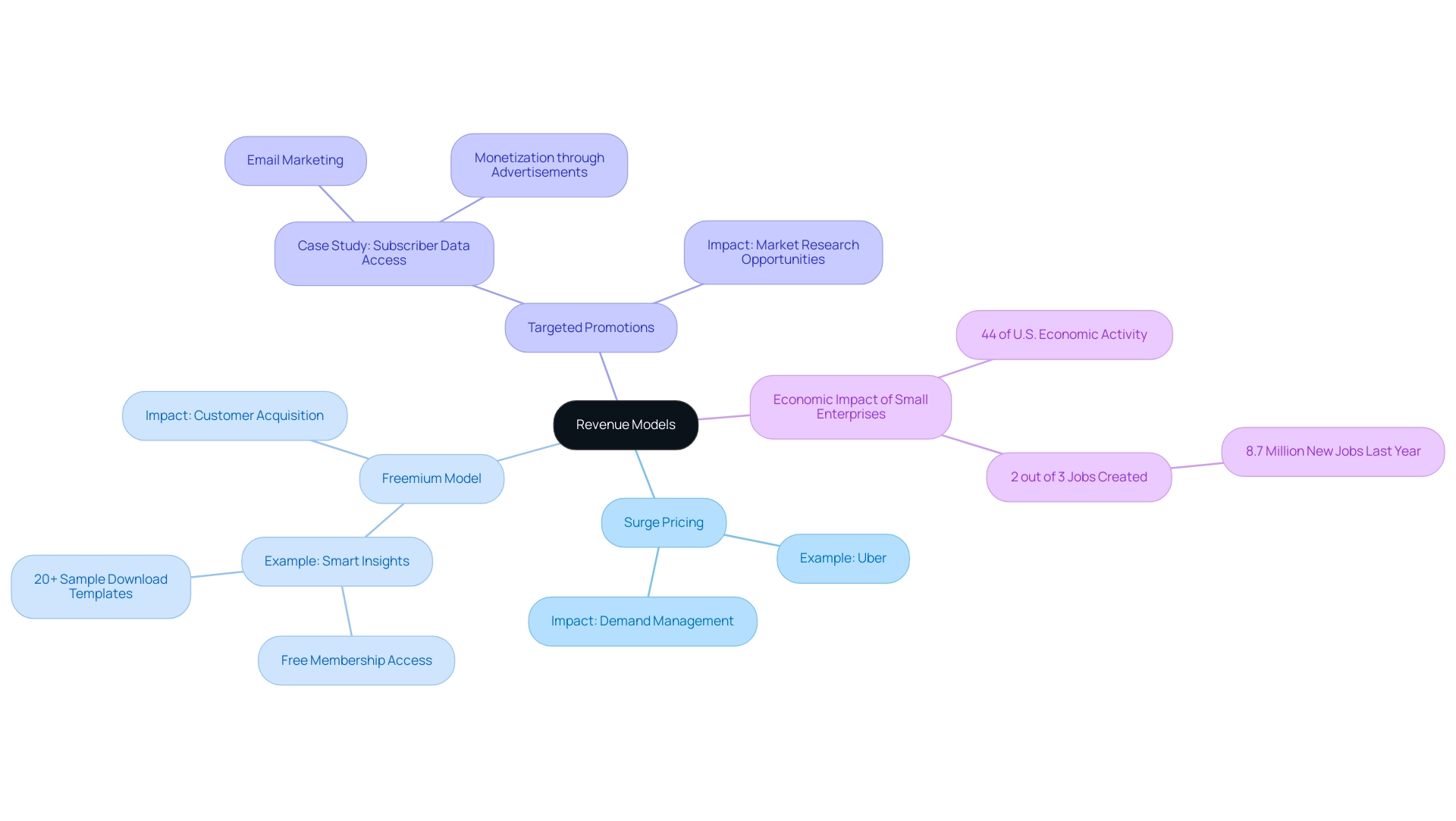
Income strategies involve different approaches, such as the sample revenue model, that companies employ to generate earnings and outline how an organization plans to obtain funds through its offerings or services. A comprehensive understanding of these frameworks is essential for businesses, as they significantly impact the sample revenue model, pricing strategies, market positioning, and overall financial health. In the technology industry, marked by swift advancements, a clear sample revenue model can distinguish prosperous companies from those that struggle to sustain profitability.
For instance, Uber effectively employs surge pricing during peak times to balance demand and supply, ensuring that riders have access to services when needed. Likewise, Smart Insights employs a freemium approach, providing complimentary membership access to more than 20 templates that exemplify a sample revenue model, which demonstrates another effective income generation strategy within the tech sector. Creating a robust financial framework not only promotes sustainable expansion but also allows enterprises to maneuver through economic variations skillfully.
Significantly, small enterprises generate two out of every three jobs in the U.S. and represent 44% of economic activity, emphasizing the necessity of strong financial strategies in fostering job creation and innovation within the sector. Furthermore, site owners can utilize customer information for targeted email promotion, as shown in a case study, enabling monetization through advertisements in newsletters and research opportunities.
Exploring Different Types of Revenue Models
Companies today can embrace a sample revenue model that incorporates a range of income strategies, each customized to particular market conditions and consumer tastes. Comprehending these frameworks is essential for startups seeking to enhance their sample revenue model and income generation strategies. Here is a summary of the main categories of income structures:
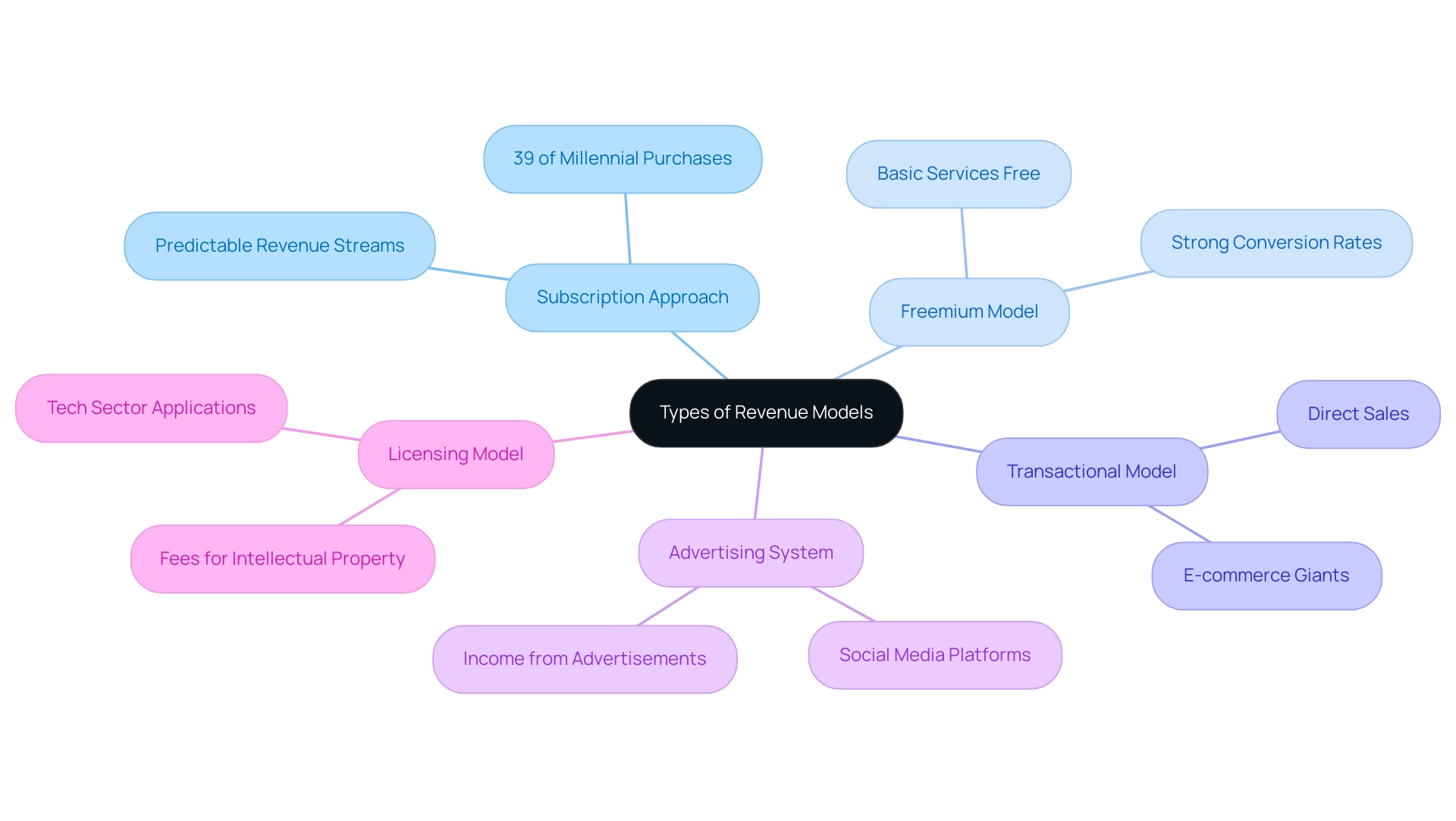
- Subscription Approach: This approach requires customers to pay a recurring fee for continuous access to a product or service. It has gained significant traction among Software as a Service (SaaS) companies, such as Netflix and Adobe, due to its ability to create predictable revenue streams. Recent statistics indicate that subscription systems are experiencing substantial growth, with a notable shift in consumer behavior, particularly among millennials, who are increasingly relying on retail subscriptions for replenishable goods, accounting for 39% of their purchasing habits.
- Freemium Model: This approach offers basic services at no cost while charging for advanced features. Companies such as Spotify and LinkedIn illustrate the success of this approach. They attract users with free access, fostering engagement and incentivizing upgrades to premium services. The effectiveness of the freemium approach is underscored by conversion rates, which are projected to remain strong in 2024.
- Transactional Model: Revenue is primarily generated through the direct sale of products or services, a method commonly utilized by e-commerce giants like Amazon. This system enables companies to take advantage of one-time purchases, catering to consumers' urgent needs.
- Advertising System: This system generates income by showing advertisements to users. Social media platforms such as Facebook have successfully leveraged this approach, creating a vast network of advertisers eager to reach targeted audiences.
- Licensing Model: Companies charge fees for the use of their intellectual property, which can include software licenses or patents. This framework is especially widespread in tech sectors where proprietary technology provides competitive benefits.
Each of these income structures can serve as a sample revenue model, offering unique benefits and being efficiently customized to align with specific business strategies. Sharon Gee, Vice President of Revenue Growth and General Manager of Omnichannel at Bigcommerce, emphasizes the importance of integrating various online experiences, stating,
Omnichannel used to mean, ‘I want to be able to sell directly to consumers, both online and offline,' that is still the case, but now there are many different flavors of online experiences that need to be integrated.
This demonstrates how developing omnichannel approaches can influence income structures.
Businesses are encouraged to experiment with various income structures and promotional strategies, such as providing discounts or lower-priced tiers, to enhance user conversion and retention; notably, 38% of consumers indicated they would have remained subscribed if presented with such options. A noteworthy case study revealed that free trials convert 61.7% of users from the first to the second month, highlighting the potential of strategic promotional tools in enhancing subscription retention rates.
Case Studies: Successful Revenue Models in Action
Exploring effective financial frameworks offers essential understanding for companies seeking to enhance their sample revenue model.
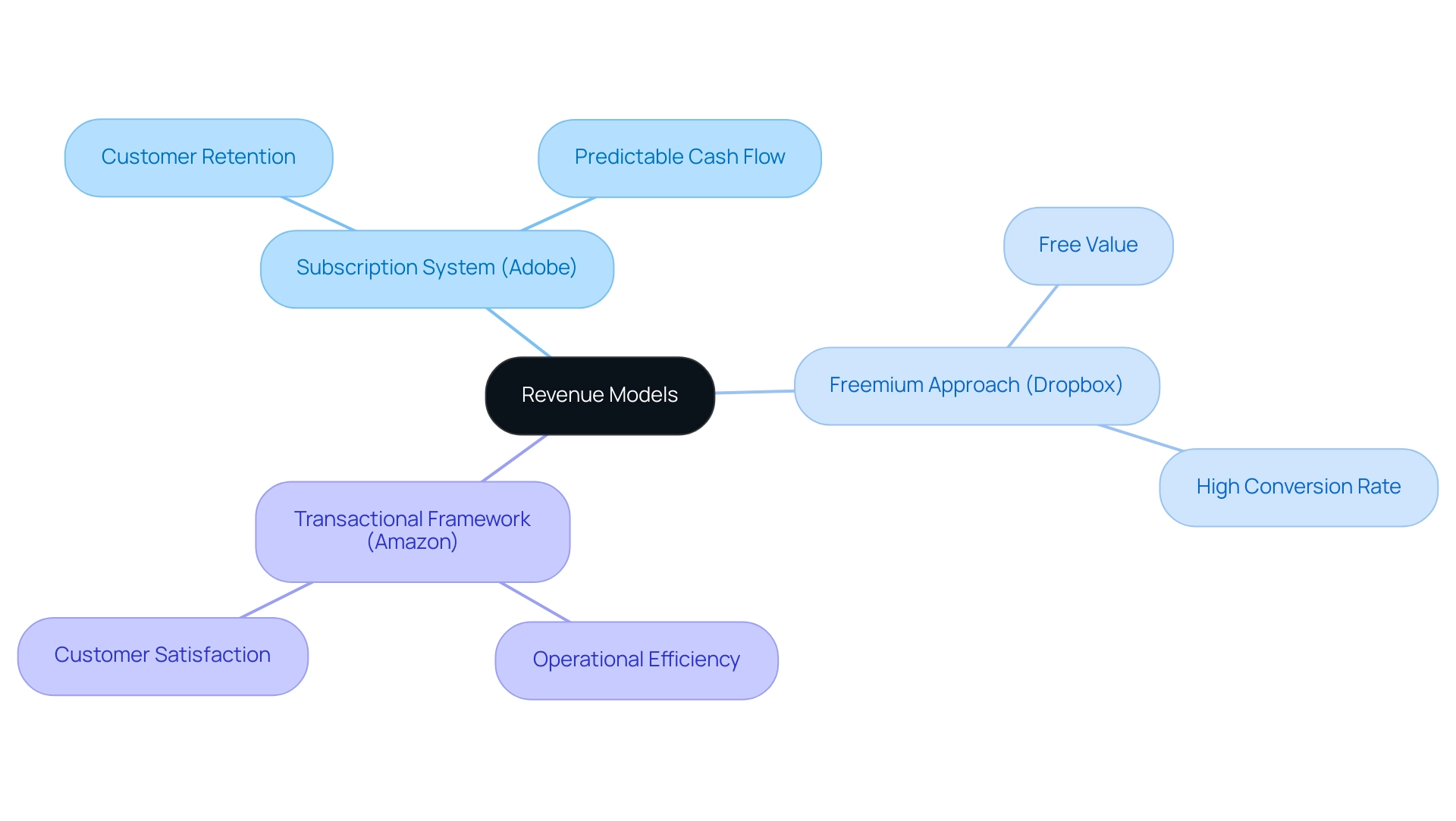
- Subscription System: Adobe's strategic transition from a one-time purchase approach to the subscription-based Adobe Creative Cloud has led to improved customer retention and the creation of dependable income streams. This transition not only fostered a loyal customer base but also contributed to predictable cash flow, a crucial factor for sustained growth. Considering recent statistics, with acquisition rates declining from 4.1% in 2021 to 2.8% in 2024, it is clear that effective financial strategies are crucial for sustaining customer acquisition.
- Freemium Approach: Dropbox exemplifies the effective use of the freemium approach by initially offering free storage space to users. This approach leads to a significant conversion rate of free users to paid plans as their storage needs increased. This framework not only expands user acquisition but also generates significant income, demonstrating the effectiveness of providing value upfront. Casey Graham, CEO of Gravy, emphasizes the importance of proactive support in revenue generation, stating, "If you want to find out how partnering with Gravy can lessen your high churn rate and give your payment recovery efforts the boost it needs, book a free coaching session today."
- Transactional Framework: Amazon's e-commerce platform is a prime example of the transactional framework, capitalizing on a vast array of products and highly efficient logistics to drive sales. This framework emphasizes how a focus on operational efficiency can lead to increased sales volume and customer satisfaction. Moreover, Gravy's case study on reducing churn demonstrates how proactive support can improve customer retention, which is vital for subscription and freemium structures.
These case studies highlight that different financial frameworks, such as a sample revenue model, can be customized to match a company's distinct value proposition and industry dynamics, offering a guide for startups and established enterprises alike.
Choosing the Right Revenue Model: Key Considerations
Choosing a suitable sample revenue model is a vital decision for enterprises, influenced by several key factors:
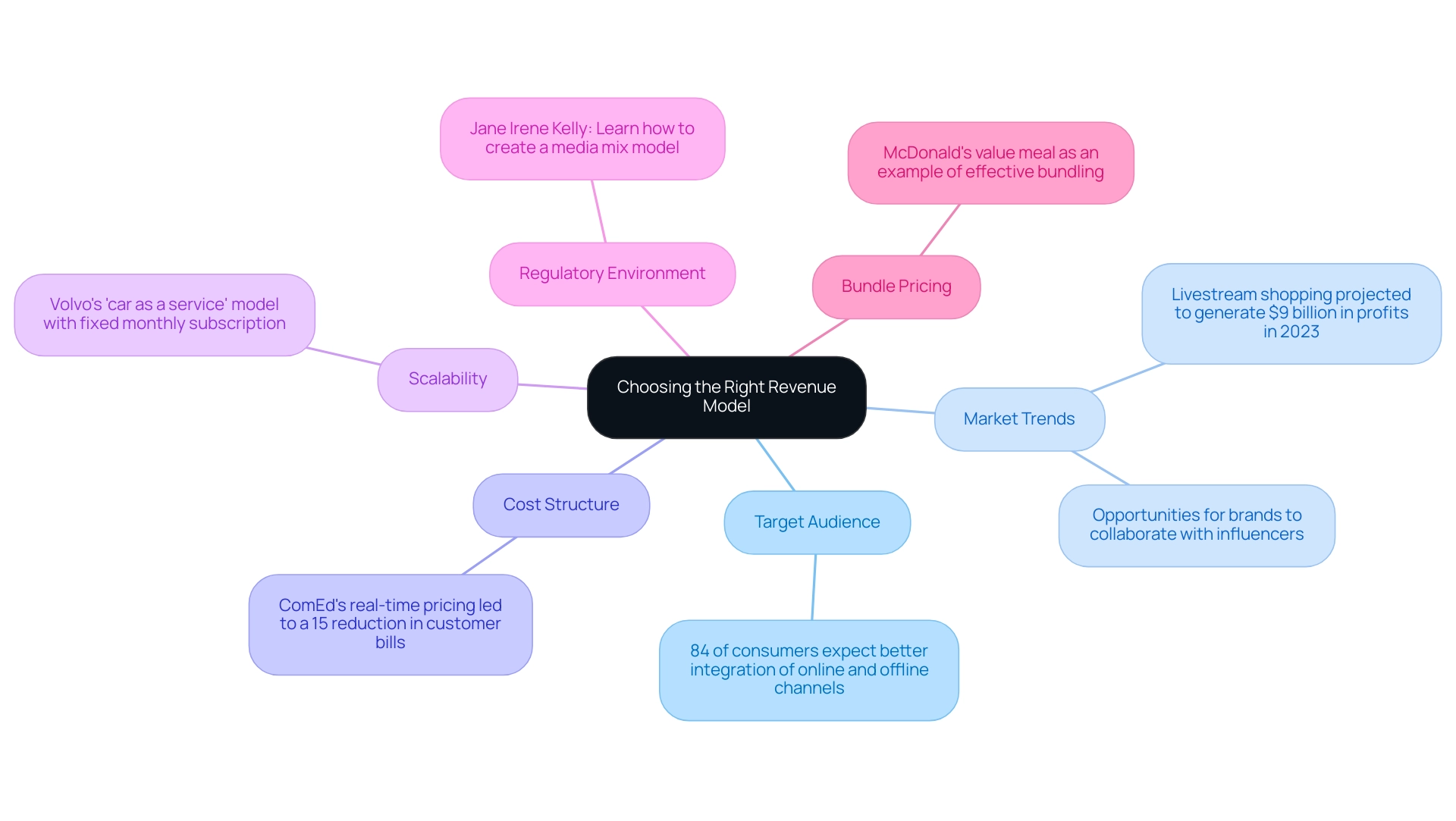
- Target Audience: A deep understanding of the target market's preferences and behaviors is essential. For example, a recent study showed that 84% of consumers anticipate retailers to improve the integration of their online and offline channels, highlighting the necessity for businesses to align their strategies accordingly.
- Market Trends: Awareness of industry trends can significantly influence selection. For example, the projected $9 billion profit from livestream shopping in 2023 illustrates a growing opportunity for brands to engage with consumers through influencer collaborations.
- Cost Structure: It is essential to evaluate the financial effects of each income approach to guarantee its sustainability. For instance, Comed's implementation of real-time pricing led to a 15% reduction in customer bills, demonstrating how effective pricing strategies can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Scalability: The selected revenue structure must be scalable, allowing for growth as the business evolves. For example, Volvo's 'car as a service' system provides a fixed monthly subscription covering all expenses, illustrating an innovative approach to scalability.
- Regulatory Environment: Finally, grasping compliance requirements is essential, as they can determine the viability of certain frameworks. As Jane Irene Kelly advises, "Learn how to create a media mix framework, and improve its accuracy with call tracking."
By carefully evaluating these elements, companies can create a sample revenue model that aligns with their strategic goals and meets the evolving needs of the industry. Additionally, the use of bundle pricing, as exemplified by McDonald's value meals, showcases an effective strategy for simplifying purchasing decisions for customers while providing value.
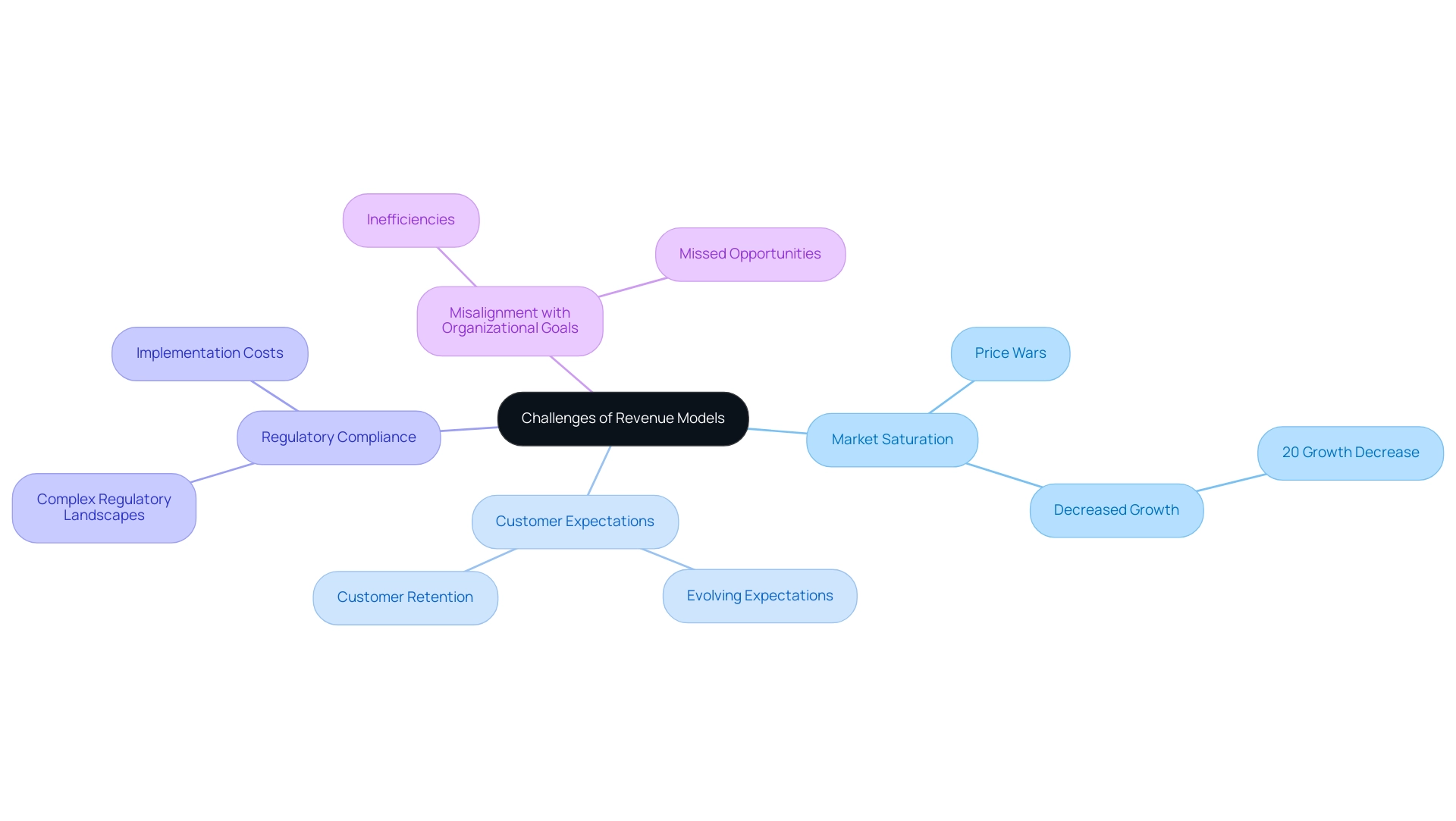
Challenges and Pitfalls of Revenue Models
Sample revenue models play an essential part in assessing the success of enterprises, yet they come with their own difficulties. One significant hurdle is market saturation; in fiercely competitive environments, distinguishing a profit strategy can prove problematic, often resulting in price wars that diminish profit margins. According to recent statistics, businesses functioning in saturated markets encounter a 20% decrease in growth compared to those in less saturated environments.
Furthermore, companies must navigate customer expectations, which are continually evolving. This is particularly crucial in subscription frameworks, where customer retention is essential for long-term sustainability. Adapting to these expectations can require substantial agility and foresight.
Another challenge lies in regulatory compliance. Companies operating across various regions face complex regulatory landscapes that can impede their operational efficiency. Additionally, the implementation costs associated with transitioning to a new revenue system can be substantial, necessitating considerable investments in technology and marketing.
For instance, a case study on self-driving vehicles indicates that firms investing in innovative designs must also prepare for significant upfront costs and regulatory hurdles, which can delay market entry and affect profitability.
Moreover, there is the risk of misalignment with organizational goals. A financial model that does not align with the company’s strategic objectives can lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Recognizing these challenges is paramount; as Shagun Sharma notes,
Awareness of saturation effects enables strategic budget allocation, improving marketing efficiency and preventing overspending in saturated channels.
By proactively tackling these issues, companies can enhance their sample revenue model and increase their likelihood of success in competitive environments. The future of business sustainability is influenced by global interconnectedness and the need for organizations to adapt to complex challenges, making it essential to remain vigilant in evolving market conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding revenue models is essential for businesses aiming to achieve sustainable growth and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace. By examining various models such as:
- Subscription
- Freemium
- Transactional
- Advertising
- Licensing
organizations can identify the most effective strategies for revenue generation tailored to their unique market dynamics and consumer preferences. Successful case studies, like those of Adobe and Dropbox, underscore the importance of these models in fostering customer loyalty and generating predictable income streams.
However, selecting the right revenue model is not without its challenges. Businesses must navigate:
- Market saturation
- Evolving customer expectations
- Regulatory compliance
- Implementation costs
By thoroughly assessing these factors, organizations can create robust revenue models that align with their strategic objectives while remaining adaptable to changing market conditions.
Ultimately, a well-defined revenue model serves as a critical foundation for any business, guiding pricing strategies, market positioning, and overall financial health. Companies that invest the time and resources to understand and implement effective revenue models are better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape, ensuring not only their survival but their long-term success.



