Overview
The article compares the hiring practices and experiences of interning at startups versus corporate companies, highlighting distinct advantages and disadvantages of each environment. It emphasizes that startups offer hands-on experience and rapid skill development due to their dynamic nature, while corporate internships provide structured roles and stability, which may cater to different career aspirations and preferences.
Introduction
The landscape of internships presents a compelling dichotomy between the vibrant world of startups and the structured environment of corporate companies.
Startups, often characterized by their innovative spirit and rapid growth, offer interns a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in a dynamic work culture where adaptability and creativity are paramount.
Conversely, corporate internships provide a more predictable framework, emphasizing structured mentorship and defined roles that can lead to clear career pathways.
As the job market continues to evolve, understanding the fundamental differences between these two environments is crucial for aspiring interns.
This article delves into the key distinctions, advantages, and challenges associated with internships at startups versus corporates, shedding light on how these experiences can shape future career opportunities.
Defining Startups and Corporate Companies: Key Differences
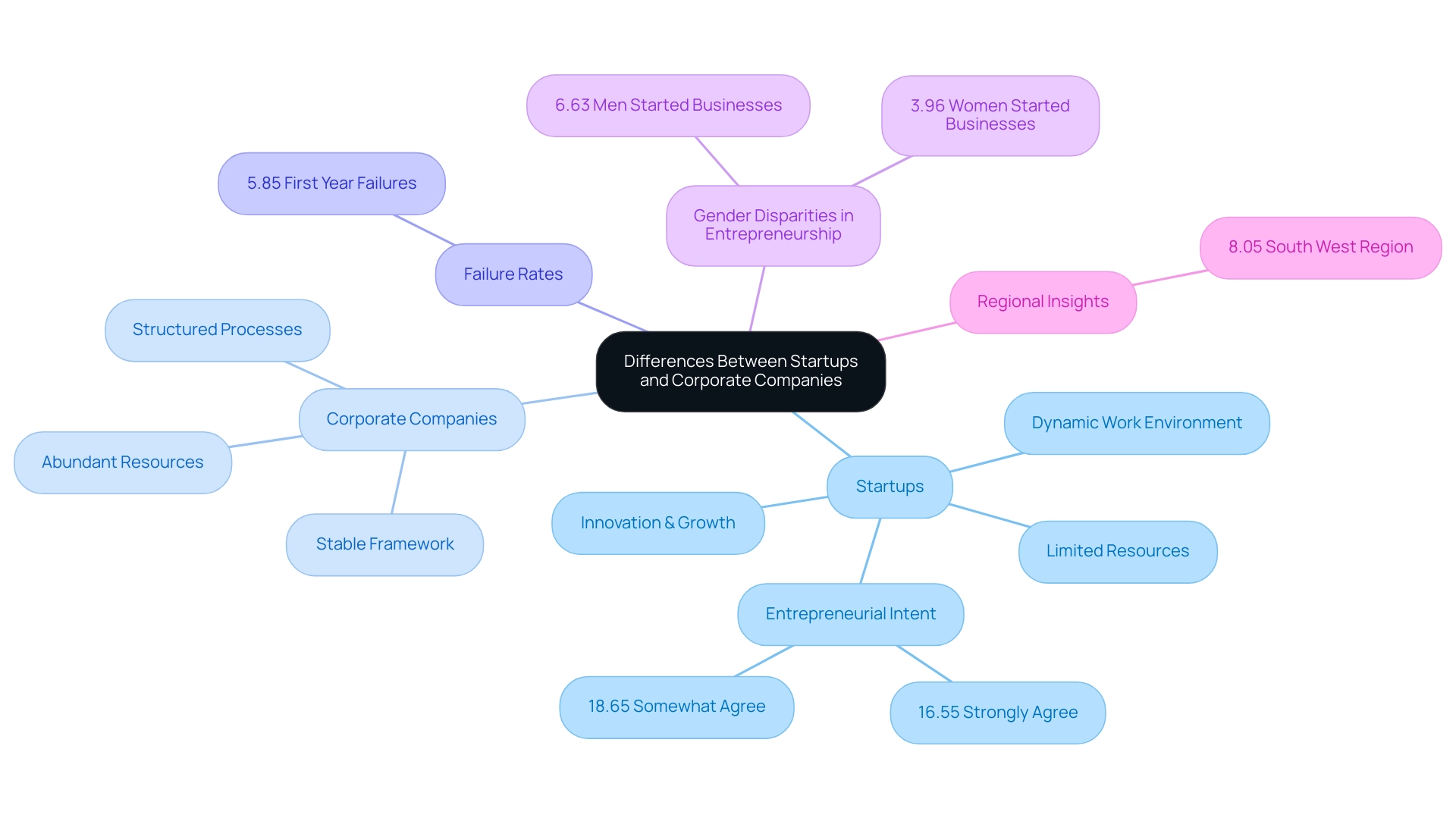
Startups are generally characterized as newly established enterprises that prioritize innovation and rapid growth. These entities often operate with limited resources, fostering a dynamic work environment where agility and adaptability are paramount. In contrast, corporate companies are well-established organizations defined by structured processes and abundant resources, functioning within a more stable framework.
This inherent distinction profoundly impacts not only the work culture but also the opportunities available in each setting. For instance, new businesses that allow individuals to intern for startups typically provide interns a hands-on experience that encourages creativity and initiative, whereas corporate internships often involve more structured tasks within established protocols. According to recent surveys:
- A significant 16.55% of respondents strongly agree
- 18.65% somewhat agree with the notion of wanting to start their own business in the future, highlighting a growing inclination towards entrepreneurial ventures.
However, it's important to note that 5.85% of all companies fail in their first year on average since 2016/17, indicating the risks associated with pursuing entrepreneurial opportunities. Furthermore, research indicates that men are more likely to initiate their own businesses compared to women, with:
- 6.63% of men
- 3.96% of women reporting having started a business.
The South West region exhibits the highest percentage of individuals who have initiated new businesses at 8.05%.
As Dr. Bagus Riyono, a psychologist and lecturer, points out,
All this was done so that the researcher could achieve comprehensive research results.
These nuances in work culture and opportunities highlight the significant distinctions that define the practical training in new businesses compared to corporate settings, further shaped by personal preferences and career aspirations.
The Pros and Cons of Interning at Startups vs. Corporates
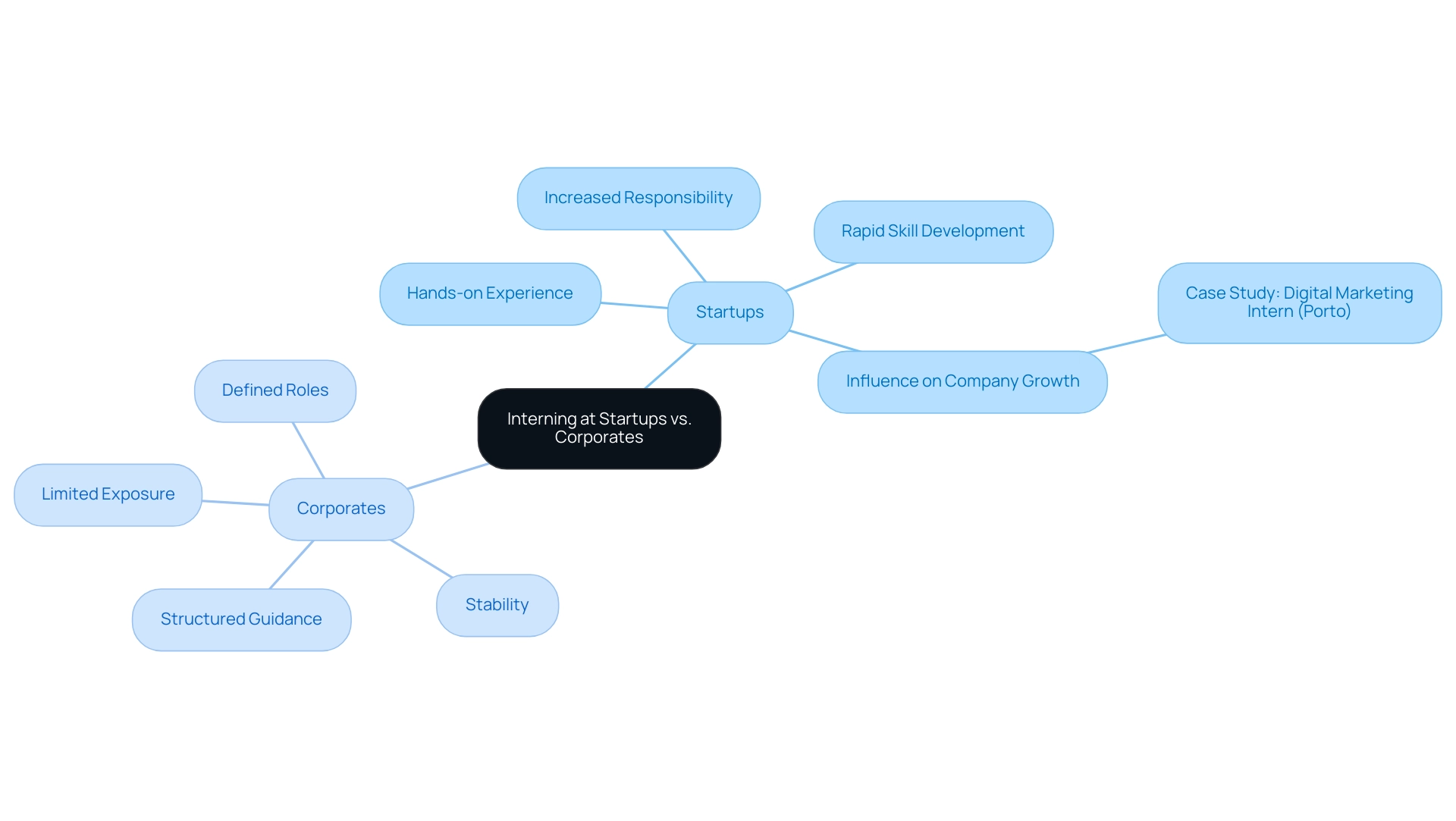
To intern for a startup presents distinct advantages, notably the opportunity for hands-on experience and increased responsibility. As an intern for a startup, individuals are often expected to take on multiple roles, which fosters rapid skill development and a deeper understanding of business operations. For instance, a recent position at a medtech company in Porto, which is a paid role commencing on 27/11/2024, centered on clinical evaluation and regulatory advancements.
This practical experience enabled participants to create a significant influence while supporting the company's growth in the U.S. market, as emphasized in a case study that illustrates the concrete advantages of early career programs.
In contrast, corporate placements usually provide more organized initiatives that feature strong guidance and a clearer path for professional development. Interns in these environments often have defined roles, which can provide a sense of stability and predictability. Nevertheless, this structure may lead to a more rigid environment, where interns find themselves confined to support roles with limited exposure to broader business functions.
As mentioned by Dave Malouf, an Interaction Designer and Co-Founder,
When it comes down to something like this, I would determine where you're going to work based on the individuals you'd be collaborating with,
underscoring the significance of team dynamics in influencing practical experiences.
Furthermore, there are current openings such as the B2B Outbound Sales Intern position in Barcelona, which requires strong Spanish skills and highlights the need for talent in emerging business environments. Ultimately, both startups and corporates provide unique learning experiences, and the choice to intern for a startup or work in a corporate environment should align with an individual's career goals and preferred working style. The landscape of work placements in 2024 will continue to evolve, with each option presenting its own set of pros and cons that merit careful consideration.
Hiring Practices: How Startups Attract and Select Interns
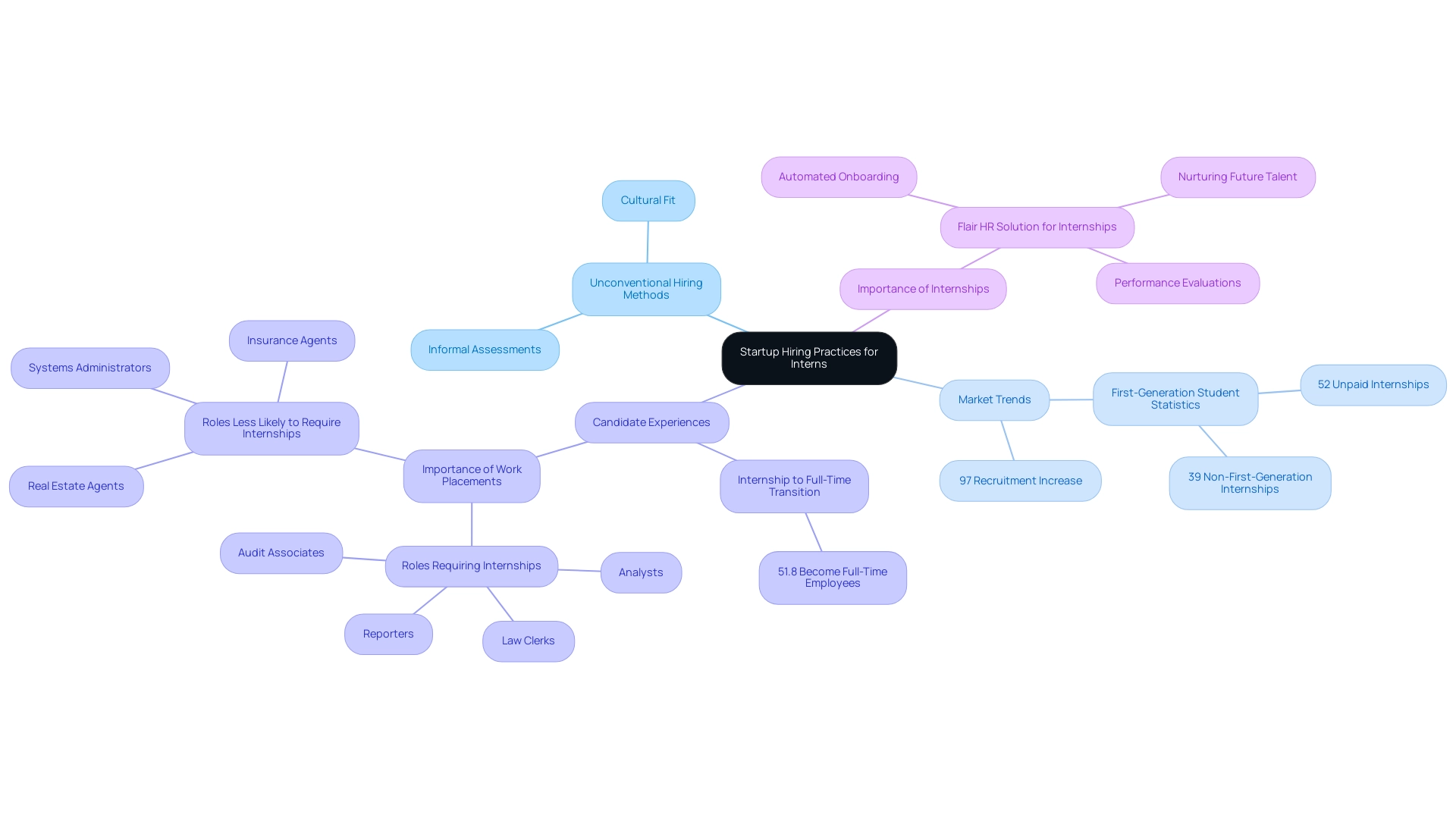
Startups frequently adopt unconventional hiring practices to attract an intern for startup roles, prioritizing cultural fit and potential talent over traditional qualifications. This approach is evidenced by a projected 97% increase in recruitment levels in sectors such as retail, FMCG, and tourism, highlighting a shift in the job market landscape. Notably, first-generation students are more likely to take unpaid internships (52%) compared to their non-first-generation counterparts (39%), showcasing the diverse experiences of internship candidates.
Startups leverage social media, networking events, and specialized online platforms to connect with candidates who resonate with their organizational values and mission, particularly those interested to intern for startup. Instead of adhering to the typical corporate structure of numerous formal interviews and standardized evaluations, emerging companies frequently participate in informal discussions or project-oriented assessments to evaluate a candidate's abilities and creativity. This informal process not only fosters a more relaxed atmosphere but also allows startups to identify individuals who are suitable to intern for startups and thrive in their dynamic environments.
In contrast, corporate hiring typically emphasizes academic credentials and rigorous screening processes, making it crucial for prospective candidates to understand these distinctions. As highlighted by the National Association of Colleges and Employers, approximately 51.8% of interns move into full-time positions after graduation, emphasizing the importance of these experiences in obtaining employment. Moreover, work placements are essential for securing positions such as law clerks, audit associates, reporters, and analysts, further emphasizing the significance of navigating the application process effectively.
A practical example of effective internship management can be seen in Flair HR Solution for Internships, which is built on Salesforce and supports various work arrangements, including internships. Flair includes automated onboarding processes and performance evaluations that assist in professionals' development, helping organizations recognize potential future employees while nurturing the next generation of talent.
Skill Development and Learning Opportunities in Startup Internships
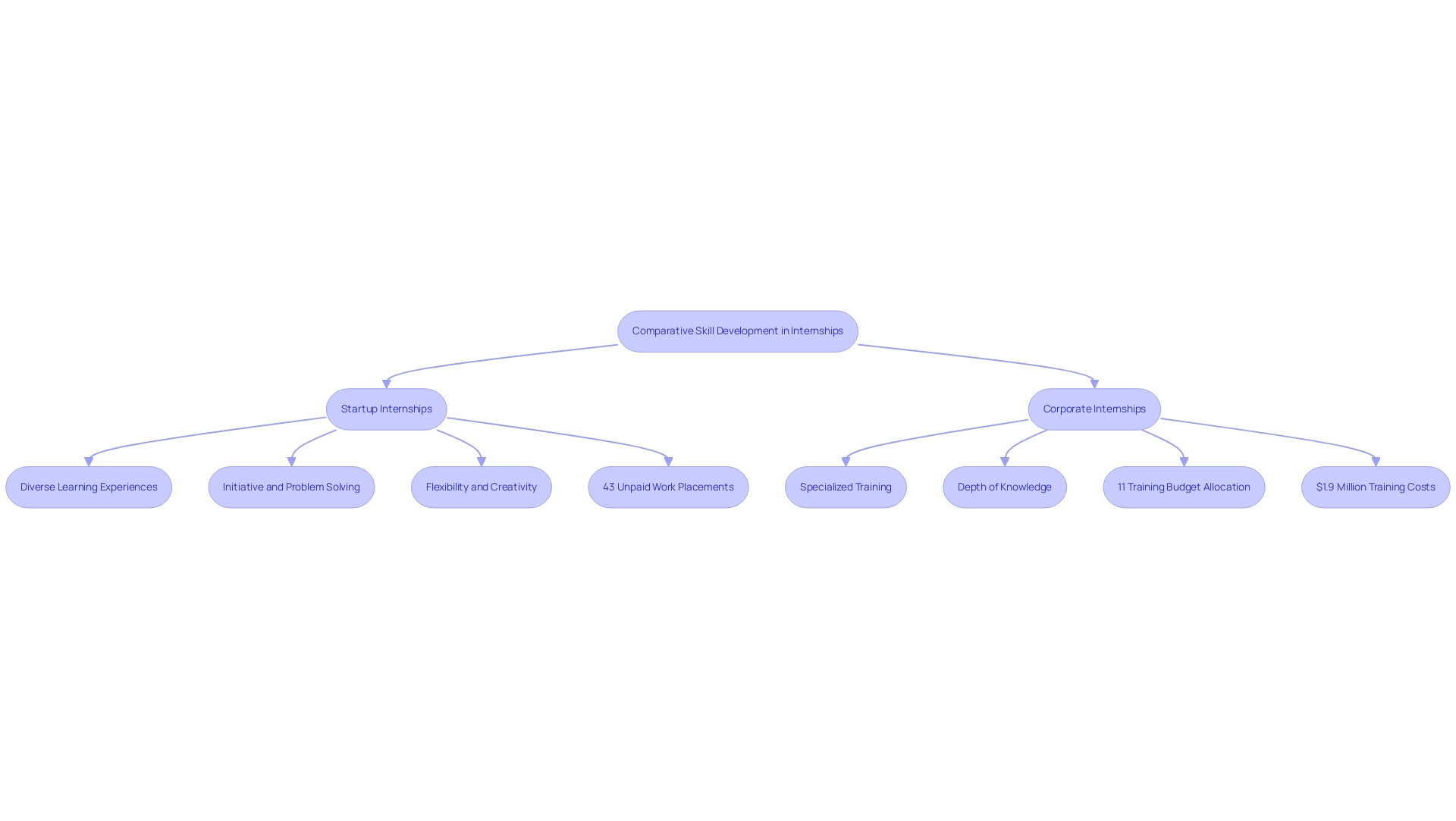
Interning for a startup is renowned for offering a diverse range of learning experiences, enabling participants to engage with various aspects of the business, from marketing strategies to product development initiatives. This dynamic environment encourages participants to take the initiative, fostering critical thinking and robust problem-solving skills. The rapid environment of new ventures requires flexibility and creativity, urging trainees to quickly address obstacles and discover answers.
In contrast, corporate programs often provide more specialized training within defined areas, resulting in a depth of knowledge that may lack the versatility found in startup settings. This disparity in skill development can have a profound impact on an intern's future employability and career trajectory. Notably, approximately 43% of work placements are unpaid, underscoring the need for careful consideration when evaluating opportunities.
Furthermore, organizations allocate 11% of their training budget to onboarding, reflecting their commitment to developing talent. Sarah Leedberg, Assistant Director of Innovation Programs at Lehigh@NasdaqCenter, emphasizes the unique advantages of early-stage company experiences, noting that each student has a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to intern for a startup and gain practical education in entrepreneurship alongside leaders who tackle real-world business challenges daily. Moreover, Flair, an HR solution designed on Salesforce, supports various work arrangements, including temporary positions, and assists in participants' professional growth, emphasizing current trends in management of such roles.
The substantial investment of $1.9 million in training costs by midsized service firms in 2023 demonstrates a strong dedication to employee development, although this may differ from the wider skill development opportunities frequently accessible in new ventures. As such, prospective interns should weigh these factors carefully when selecting their preferred internship path.
Career Impact: How Startup Internships Shape Future Opportunities
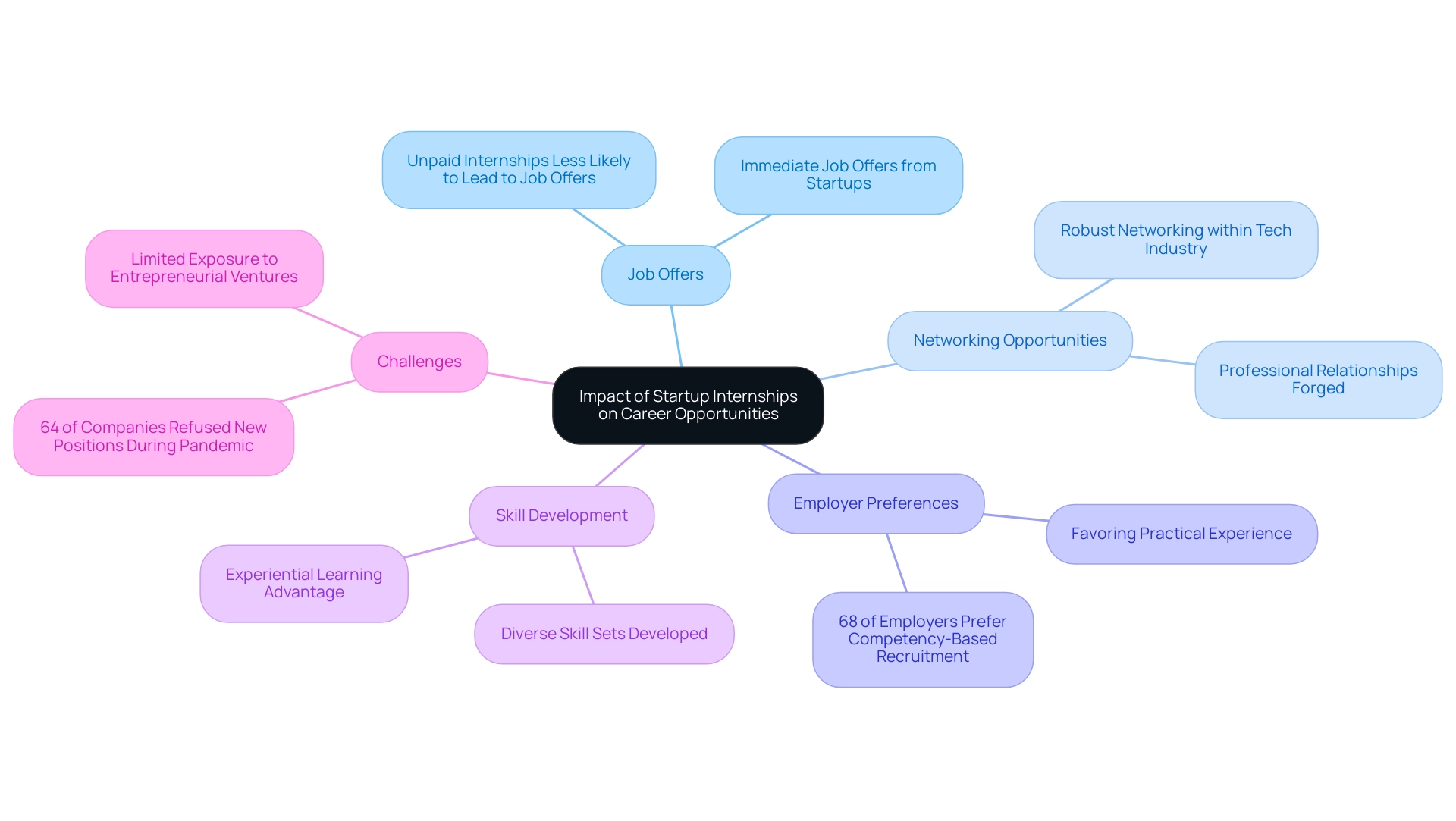
Interning for a startup often paves the way for immediate job offers and robust networking opportunities within the tech industry. The dynamic environment of startups fosters the development of diverse skill sets for those who intern for startups, which are increasingly favored by employers; notably, a significant 68% of employers now employ a competency-based recruitment approach when evaluating candidates. This trend reflects the growing importance of practical experience in hiring decisions.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that 64% of companies globally refused to offer new positions during the pandemic, highlighting the challenges faced in the placement landscape. In contrast, corporate placements may carry the advantage of a recognized brand on a resume, facilitating entry into more traditional sectors. These organized activities can limit exposure to entrepreneurial ventures, which are essential for innovation.
While unpaid work opportunities may result in fewer job offers compared to paid counterparts, they still offer invaluable knowledge and networking possibilities. As outlined in the case study 'Unpaid Internships: Worth the Investment? The feasibility of these placements varies, and although they may not be financially viable for all students, they remain a significant avenue for skill development and networking opportunities.
Ultimately, the impact of an internship for a startup on career trajectories is shaped by individual goals, skills acquired, and the professional relationships forged during the experience. It’s safe to say that this experiential learning journey gives people an advantage in the workplace and in life.
Conclusion
Internships play a pivotal role in shaping the career trajectories of aspiring professionals, and understanding the differences between startup and corporate environments is essential for making informed decisions. Startups offer a unique blend of hands-on experience and rapid skill development, encouraging interns to embrace creativity and adaptability. These dynamic settings often lead to immediate job offers and valuable networking opportunities, particularly in the tech sector, where competencies are increasingly prioritized by employers.
Conversely, corporate internships provide a more structured framework, with defined roles and robust mentorship that can lead to clear career pathways. While these environments may offer stability, they can sometimes limit exposure to broader business functions and innovative ventures. Each option presents distinct advantages and challenges, making it crucial for interns to align their choices with personal career goals and preferred working styles.
Ultimately, the decision to pursue an internship at a startup or a corporate entity should be guided by individual aspirations and the desired learning outcomes. As the internship landscape continues to evolve, both paths remain significant in equipping interns with the skills and experiences necessary for future success. Emphasizing the importance of these formative experiences can empower aspiring professionals to navigate their career journeys with confidence.



