Overview
Acquihiring is a talent acquisition strategy where companies acquire other firms primarily to leverage their skilled workforce, rather than their products or services, and has become increasingly popular in the tech sector due to the high demand for specialized skills. The article explains that this approach not only allows for rapid team integration and innovation but also addresses skill gaps, while highlighting the importance of cultural preservation and strategic alignment during the acquisition process to ensure successful outcomes.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of talent acquisition, acquihiring has emerged as a strategic approach that prioritizes the acquisition of skilled personnel over traditional product-focused mergers. This practice has gained prominence, particularly within the technology sector, where the demand for specialized skills continues to surge.
By integrating established teams, companies can not only address immediate skill shortages but also foster innovation and enhance competitive advantage. However, while the benefits of acquihiring are substantial, organizations must navigate the complexities of cultural integration and legal considerations to fully realize its potential.
This article delves into the nuances of acquihiring, exploring its strategic rationale, key distinctions from traditional acquisitions, and the challenges and benefits that come with this modern approach to talent acquisition.
What is Acquihiring? An Overview of Talent Acquisition Strategies
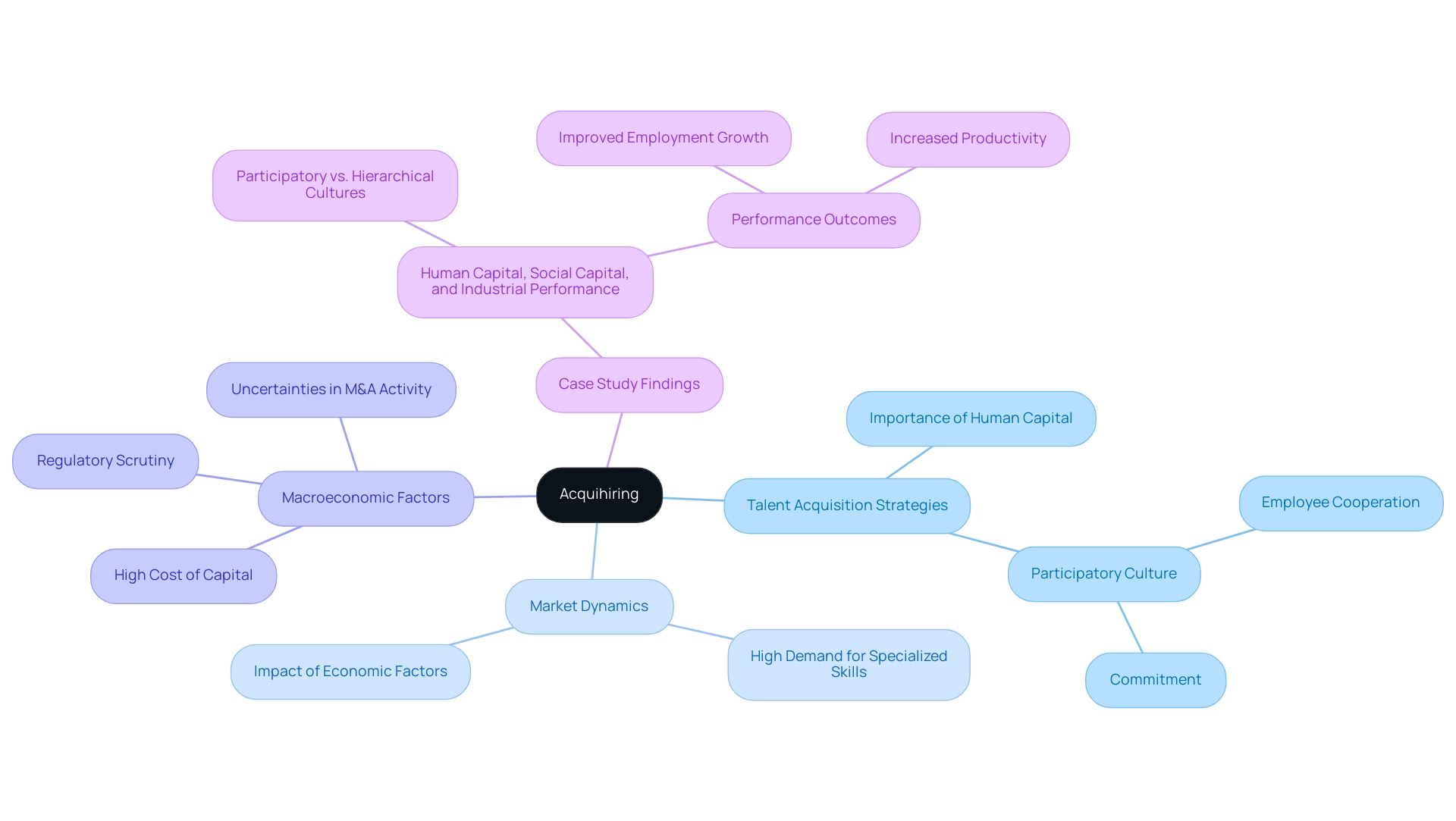
Acquihiring is a strategic approach where an organization primarily acquires another to leverage the skills and expertise of its staff, rather than focusing on its products or services. This approach has gained significant traction in the technology sector, where acquihire is driven by the high demand for specialized skills. By participating in talent acquisition, companies aim to assimilate a skilled workforce that can bolster their capabilities and foster innovation within their operations.
This dynamic capability not only helps firms sustain competitive advantage by effectively managing human capital but also aligns with the growing market dynamics that emphasize the importance of talent acquisition strategies. Win Chevapravatdumrong, Partner & Head of Legal, notes that "M&A activity slowed down considerably in recent months due to the high cost of capital, macroeconomic uncertainties, and, to a lesser extent, heightened regulatory scrutiny." This context is crucial as it highlights the current challenges that may impact hiring strategies.
Furthermore, a case study titled "Human Capital, Social Capital, and Industrial Performance" demonstrates that startups with a participatory culture, which emphasizes employee cooperation and commitment, perform significantly better than those with traditional hierarchical structures. This discovery highlights the essential importance of human capital in talent acquisition, as organizations aim to incorporate high-performance management practices within a structure that appreciates social capital.
The Strategic Rationale: Why Companies Choose Acquihiring
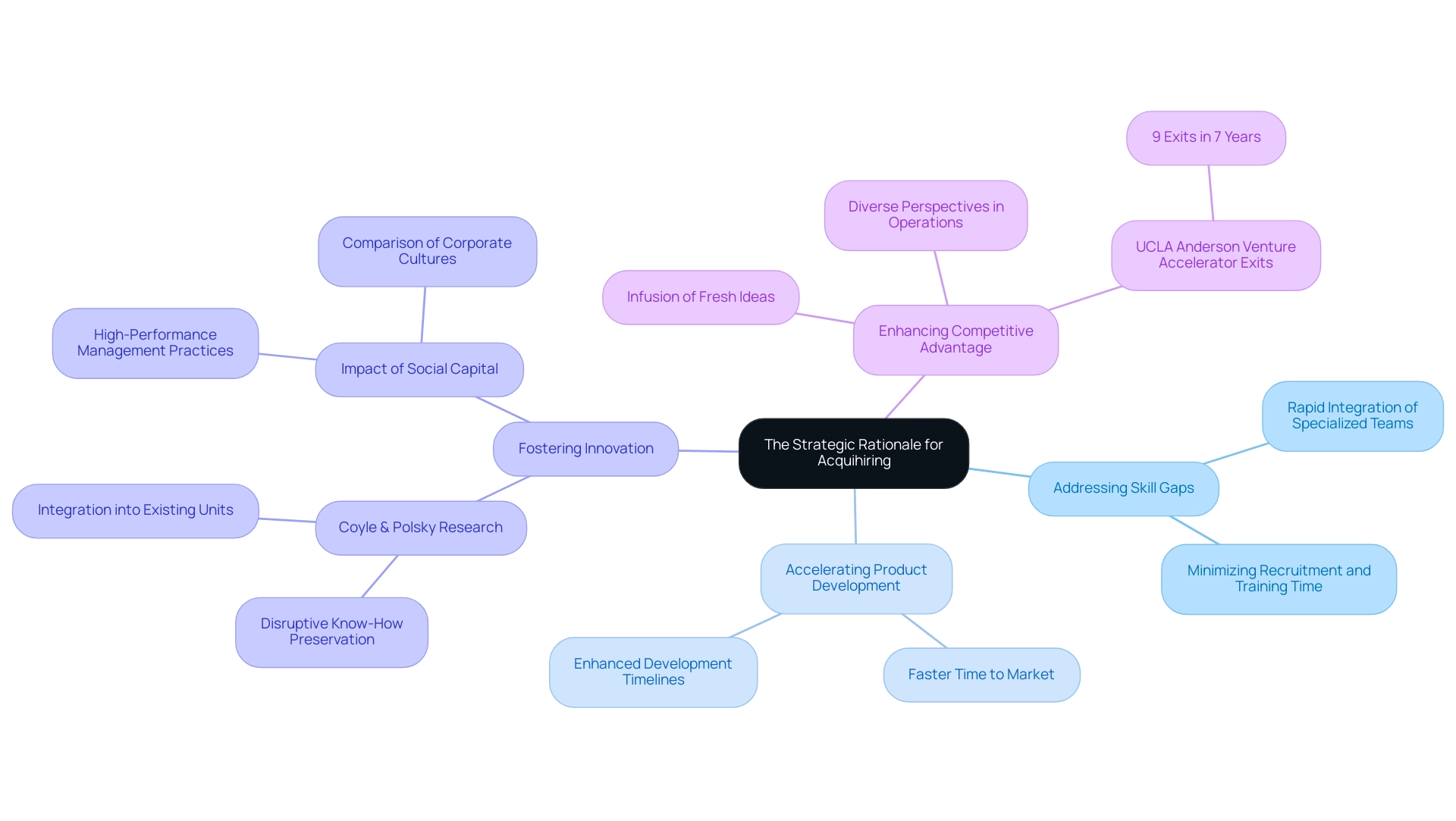
In 2024, organizations are increasingly resorting to talent acquisition as a strategic solution to address significant skill gaps within the tech industry. This approach not only facilitates the rapid integration of teams with specialized expertise but also accelerates product development timelines. By acquiring established teams, organizations can minimize the time and resources typically allocated to recruitment and training processes.
Notably, research conducted by Coyle & Polsky highlights that when a startup possesses disruptive know-how, the acquihired team is preserved and seamlessly integrated into the acquirer's existing business unit, fostering a culture of innovation. Furthermore, the success of talent acquisition strategies is evidenced by the Venture Accelerator at UCLA Anderson, which has achieved 9 exits in 7 years of operating. Embracing talent acquisition can significantly enhance a company's competitive advantage by infusing fresh ideas and diverse perspectives into its operations.
This strategic move not only addresses immediate skill shortages but also positions organizations to drive long-term growth and innovation in an increasingly competitive market. Additionally, the case study titled "Human Capital, Social Capital, and Industrial Performance" demonstrates that startups with social capital cultures significantly outperform those with hierarchical cultures, underscoring the positive impact of high-performance management practices associated with acquihire.
Acquihiring vs. Traditional Acquisitions: Key Differences
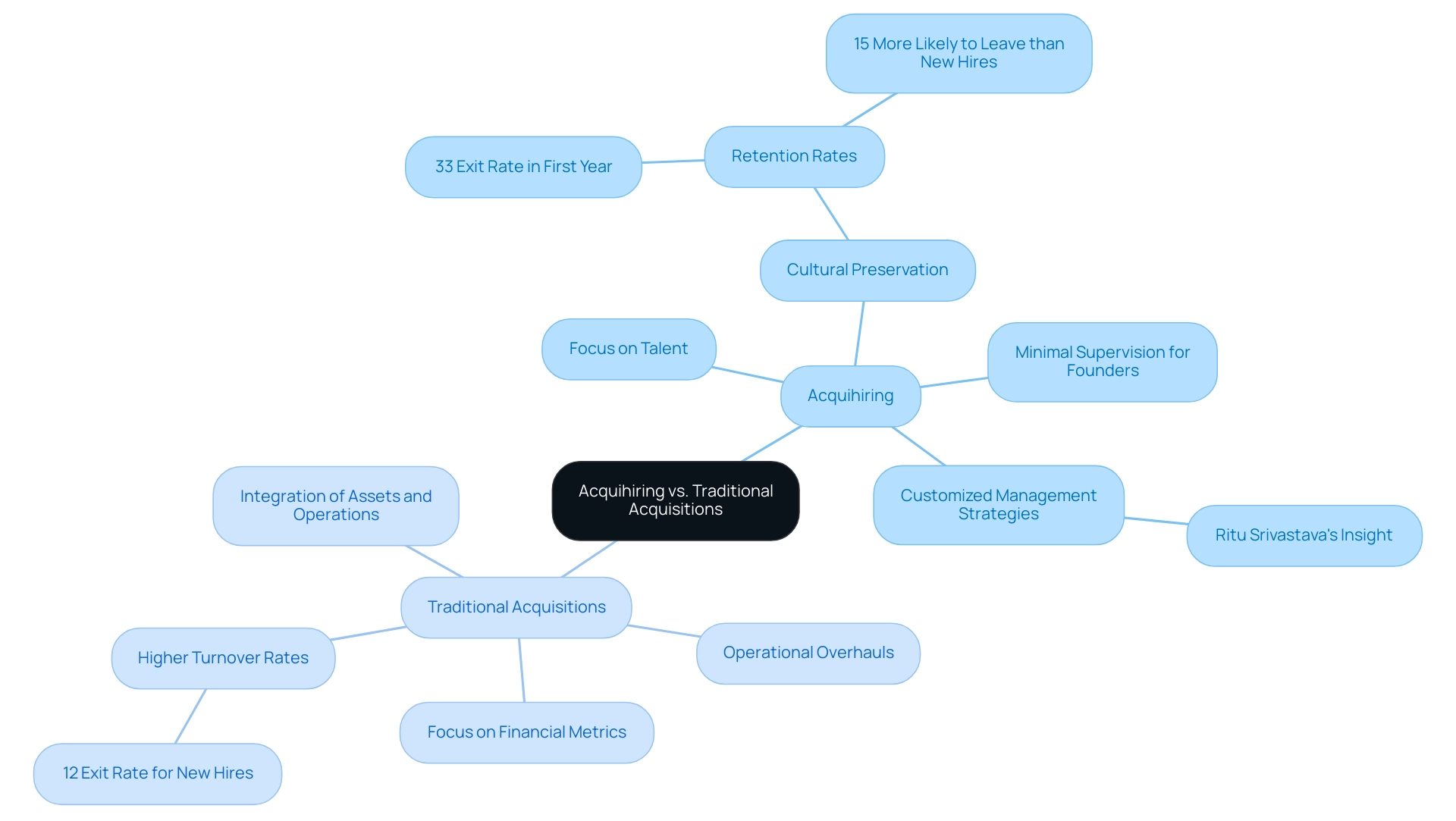
Acquihiring represents a distinct approach compared to traditional purchases, primarily emphasizing the acquisition of talent and intellectual property rather than focusing on financial metrics and market share. This model not only benefits the acquiring firm by integrating skilled personnel but also provides advantages for the founders, as it offers them motivation and minimal supervision post-acquisition. Traditional purchases typically aim to integrate the assets and operations of the obtained company, often resulting in significant operational overhauls.
Conversely, the acquihire model prioritizes maintaining the acquired team's culture, which is crucial for maximizing retention and productivity. This emphasis on cultural preservation is especially pertinent, as studies show that:
- 33% of employees exit their roles within the first year after a takeover, significantly exceeding the 12% turnover rate among comparably skilled newcomers.
The research, carried out by MIT Sloan, examined 4,000 high-tech startup purchases in the U.S. from 1990 to 2011, revealing that acquired workers are 15% more likely to leave than new hires over a three-year period.
This indicates that although conventional purchasing strategies may result in significant restructuring, hiring initiatives seek to reduce disruption and promote continuity, ultimately aiming for a more seamless integration of skills into the receiving organization. As Ritu Srivastava, cofounder of Obino, observes, 'Entrepreneurs need to be handled differently,' emphasizing the significance of customized strategies in managing acquired skills. Moreover, as highlighted by Daniel Kim, assessing the suitability of such strategies is crucial for successful mergers and acquisitions, particularly in the present environment where the financial performance of acquiring organizations is under scrutiny.
Benefits and Challenges of Acquihiring: A Dual Perspective
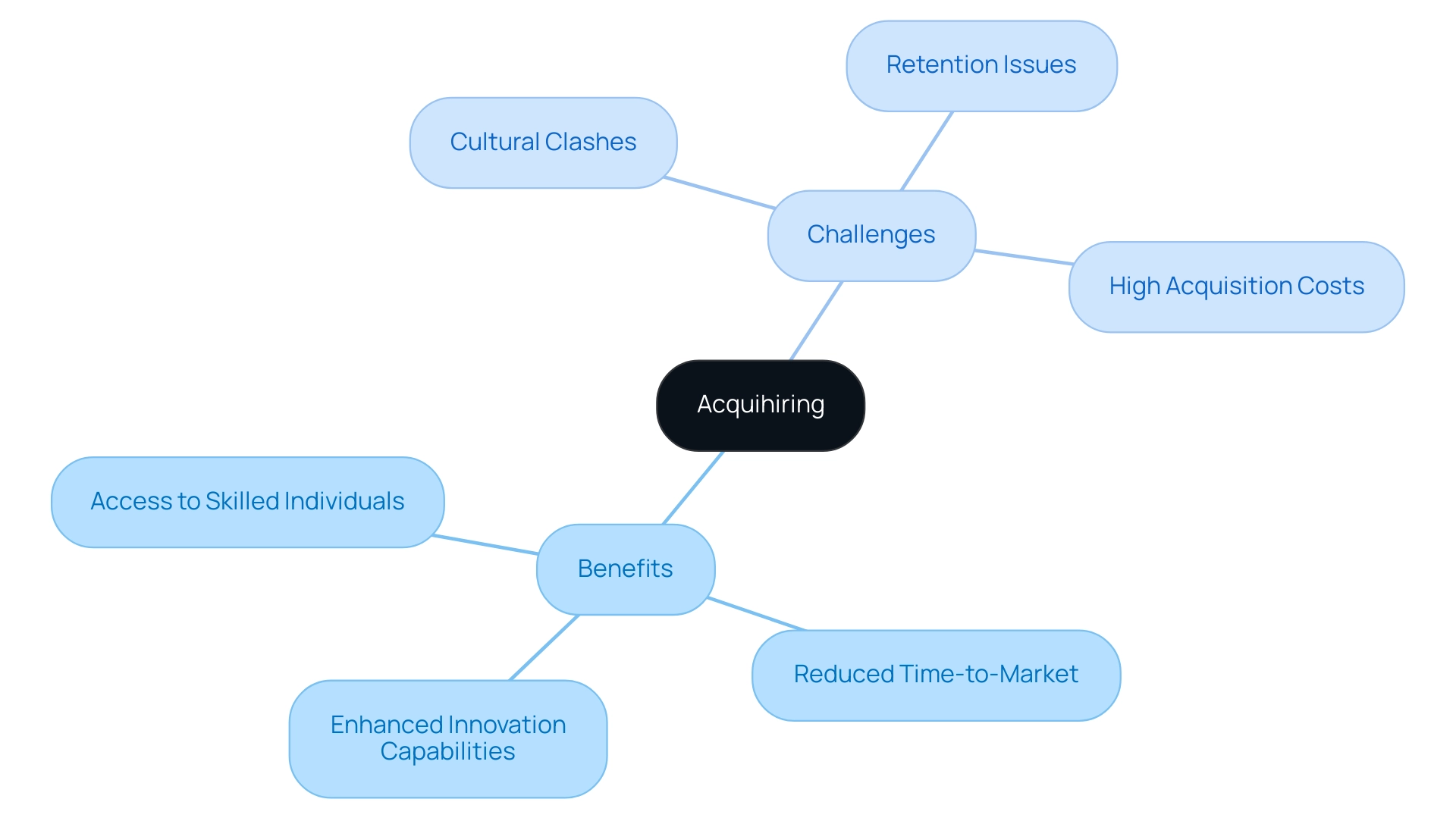
Acquihire strategies provide a variety of important benefits for businesses, especially in 2024, such as immediate access to skilled individuals, which can be essential for fostering innovation and sustaining competitive edge. By acquiring teams that are already cohesive, organizations can substantially reduce the time-to-market for new products, enabling them to respond swiftly to market demands. According to recent industry insights, companies that focus on acquihire are positioned to enhance their innovation capabilities through the integration of diverse expertise.
For example, the independent recruitment agency has a turnover of £4,000,000, highlighting the financial stakes involved in talent procurement. However, these benefits are accompanied by notable challenges.
- Cultural clashes between the acquiring and acquired teams can hamper integration efforts, leading to potential conflicts that undermine productivity.
- Retention issues may arise if employees feel uncertain about their roles within the new organizational structure, which can be exacerbated by the high costs associated with the acquisition process.
As highlighted by Coyle & Polsky, the nature of the know-how being acquired plays a critical role; if the acquired skill set is deemed disruptive, organizations are more likely to preserve the team and elevate the founder to a significant position within the parent firm. This illustrates the importance of strategic alignment and cultural compatibility in successful acquisition ventures.
Moreover, a case study named 'Owner Fatigue and Exit Plans' demonstrates that economic pressures have prompted many SMEs to contemplate selling their businesses, which highlights the significance of strategic hiring as an option for securing skills and innovation. Additionally, proposed contractual innovations aim to enhance investors' share of the acquihire process, emphasizing the strategic considerations that organizations must evaluate to ensure effective integration and unlock the long-term benefits that acquihire can offer.
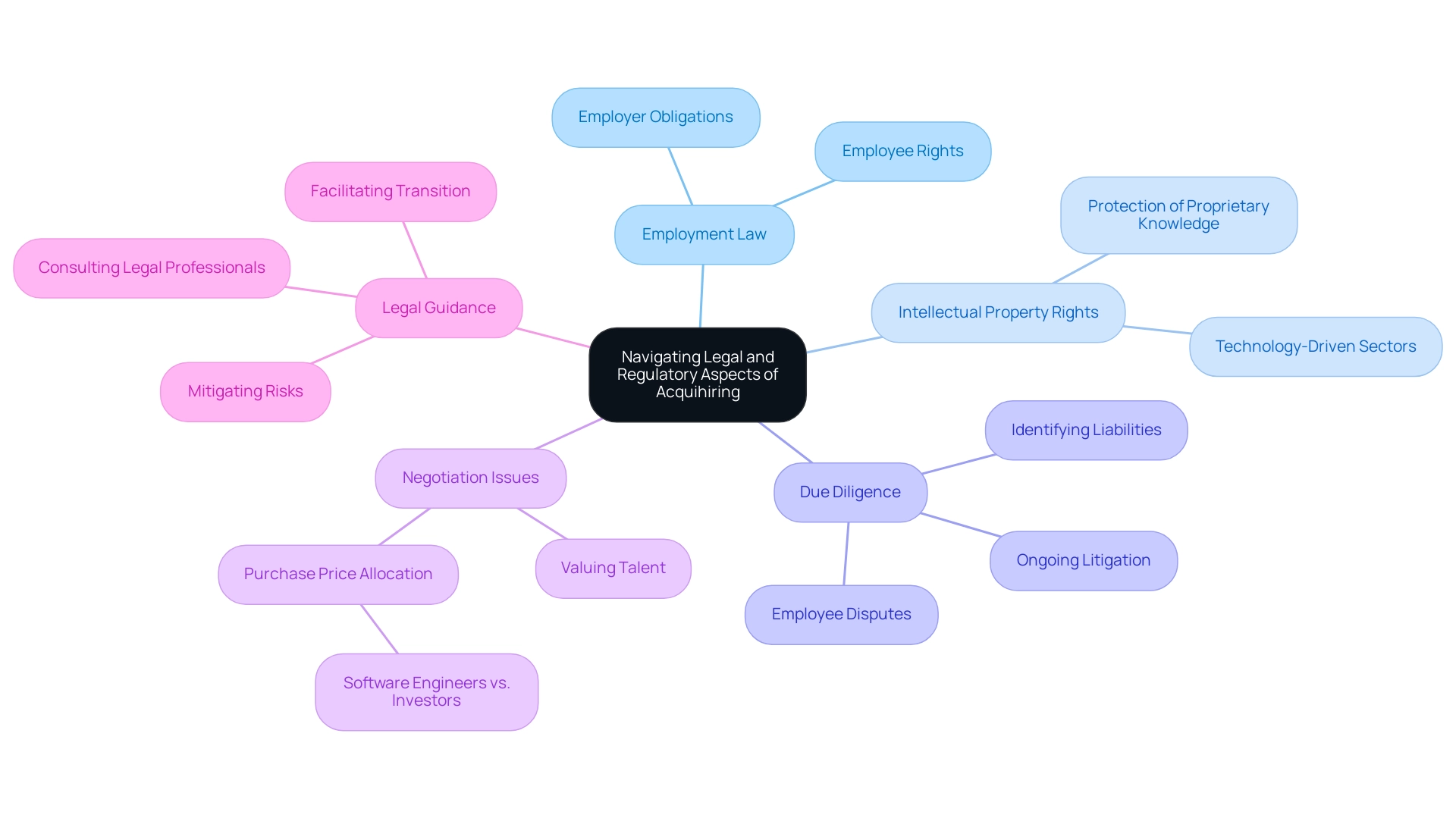
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Acquihiring
Acquihire transactions present a myriad of legal and regulatory considerations that are crucial for ensuring compliance and safeguarding the interests of both the acquiring company and the integrated personnel. As a strategic mechanism for firms to obtain talented human resources, a comprehensive understanding of employment law is essential, as it governs the rights and obligations of employees and employers. Additionally, protecting intellectual property rights is paramount, particularly in technology-driven sectors where proprietary knowledge can be a significant asset.
It is essential for firms to conduct thorough due diligence to uncover any potential liabilities associated with the acquired team, including ongoing litigation or employee disputes. As articulated by legal expert John F. Coyle, we then consider the most significant negotiation issue in acquihire transactions: how the buyer's aggregate purchase price will be allocated between the startup's software engineers and its outside investors. This highlights the complexity of valuing talent within the broader context of the acquisition.
Significantly, PayPal's recent profitability, exceeding $7 billion in merely three months, illustrates the potential success of strategic talent acquisition. Furthermore, the authors predict that a norm for allocating the purchase price will develop, proposing contractual innovations to enhance investors' shares. To navigate these challenges effectively, companies should consult with legal professionals during the acquihire process.
Such expert guidance not only mitigates risks but also facilitates a smoother transition, ensuring that both the acquiring entity and the talent being integrated can operate effectively within the new organizational framework.
Conclusion
Acquihiring has emerged as a pivotal strategy in the realm of talent acquisition, particularly within the technology sector, where the need for specialized skills is paramount. By prioritizing the acquisition of teams over products, companies can directly address skill shortages and foster innovation. This approach not only allows for a quicker integration of talent but also enhances competitive advantage, as evidenced by successful case studies that highlight the positive impact of cohesive teams on organizational performance.
The distinctions between acquihiring and traditional acquisitions are significant. While traditional methods often lead to substantial restructuring and cultural clashes, acquihiring emphasizes the retention of team culture, which is vital for maintaining employee morale and productivity. The statistics concerning employee turnover post-acquisition underline the necessity for organizations to adopt tailored strategies that prioritize cultural compatibility and strategic alignment.
However, the benefits of acquihiring come with their own set of challenges. Companies must navigate potential cultural conflicts, retention issues, and the complexities of legal and regulatory frameworks. Thorough due diligence and expert legal guidance are essential to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth integration process.
In conclusion, acquihiring stands out as a modern and strategic approach to talent acquisition that not only addresses immediate skill gaps but also supports long-term growth and innovation. As organizations continue to adapt to the evolving market landscape, understanding and effectively implementing acquihiring strategies will be crucial for sustaining competitive advantage and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.



