Overview
The article provides a comprehensive guide on how to create a balance sheet, emphasizing its importance for tech investors in assessing a company's financial health. It outlines the step-by-step process of compiling the balance sheet, including gathering monetary data, categorizing assets and liabilities, and calculating equity, while also highlighting the significance of regular reviews to adapt investment strategies based on evolving market conditions and financial metrics.
Introduction
In the intricate world of finance, the balance sheet stands as a cornerstone for understanding a company's fiscal health. This vital document encapsulates a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity, revealing insights that are crucial for tech investors navigating a rapidly evolving market. As financial landscapes shift and corporate resilience strengthens, grasping the nuances of balance sheets has never been more essential.
With the net debt to earnings ratio at a historic low and the tech sector adapting to new economic realities, investors must harness the power of this financial statement to make informed decisions. From analyzing key components to avoiding common pitfalls, the journey through balance sheet mastery is not just a necessity—it's a strategic advantage in today’s competitive investment arena.
Understanding the Balance Sheet: A Key Financial Statement
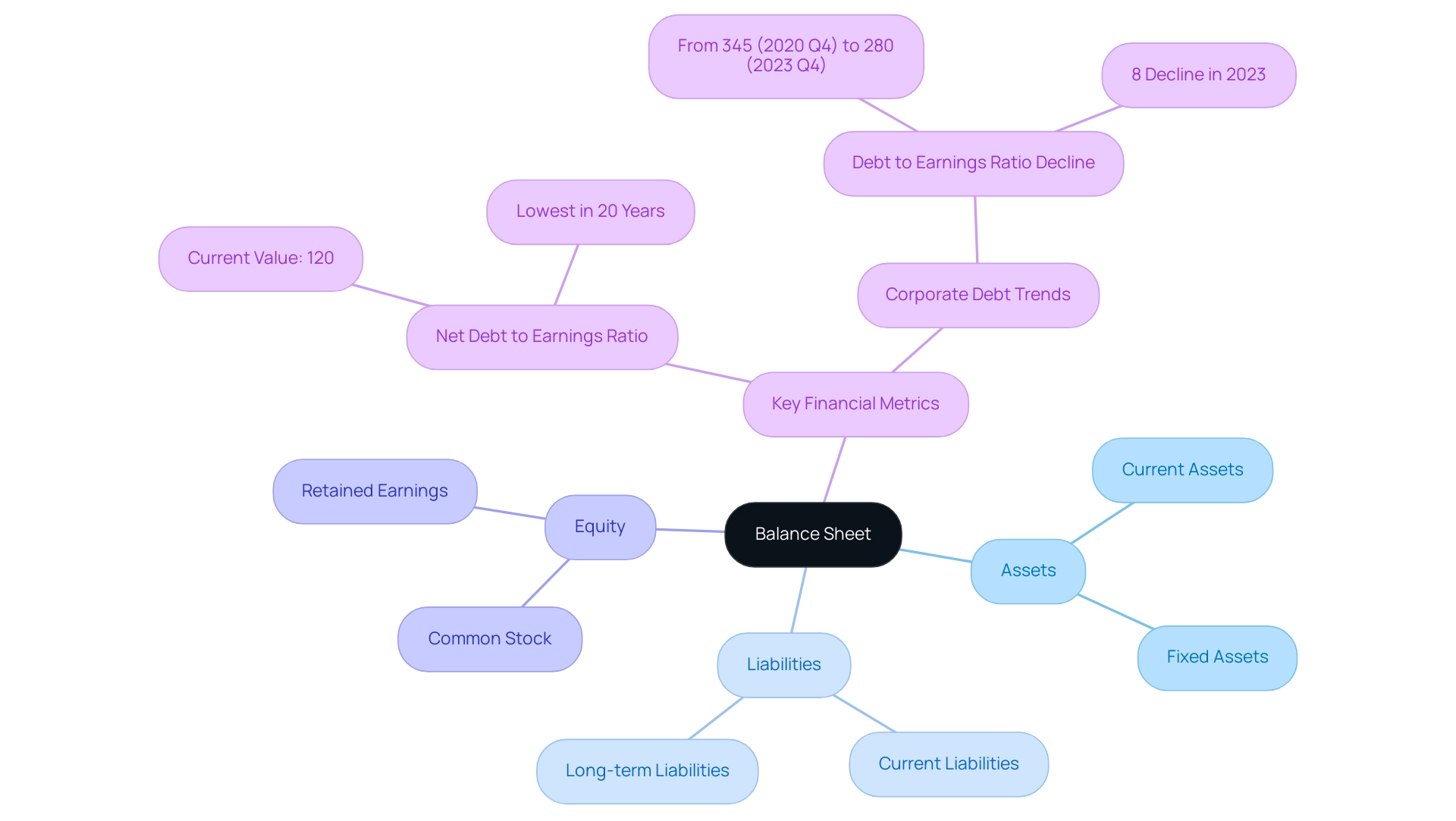
An accounting statement is a crucial report that helps illustrate how to make a balance sheet by summarizing a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular point in time. This document is meticulously structured to demonstrate how to make a balance sheet by reflecting the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. For technology investors, the financial statement is not just a formality; it is an essential tool that uncovers the fiscal stability and overall performance of a company, thus aiding informed investment choices.
Comprehending how to make a balance sheet and interpret a financial statement empowers investors to assess the fiscal health of potential investments effectively. In 2024, the importance of balance sheets is underscored by the fact that the net debt to earnings ratio has reached its lowest point in two decades, standing at approximately 120%. This statistic highlights a broader trend of improving corporate resilience, as evidenced by a significant 8% decline in corporate debt to earnings ratios in the UK during 2023.
Such metrics are essential for investors who are keen on identifying financially sound tech companies capable of withstanding market fluctuations. Additionally, the Policy Committee (FPC) emphasizes that mortgage lenders should ensure that no more than 15% of their new residential mortgages are at loan to income ratios at or above 4.5, which underscores the importance of prudent lending practices in maintaining economic stability. Furthermore, a system-wide exploratory scenario exercise has been launched to better understand the behavior of banks and non-banks during severe market shocks, which is vital for assessing the broader economic environment.
The case study titled 'UK Corporate Debt Vulnerabilities' demonstrates that corporate resilience has improved, with corporate gross debt to earnings ratio decreasing from 345% in 2020 Q4 to around 280% in 2023 Q4. Such insights obtained from accounting records remain essential to learning how to make a balance sheet while navigating investment environments as market conditions change.
Why a Balance Sheet Matters for Tech Investors
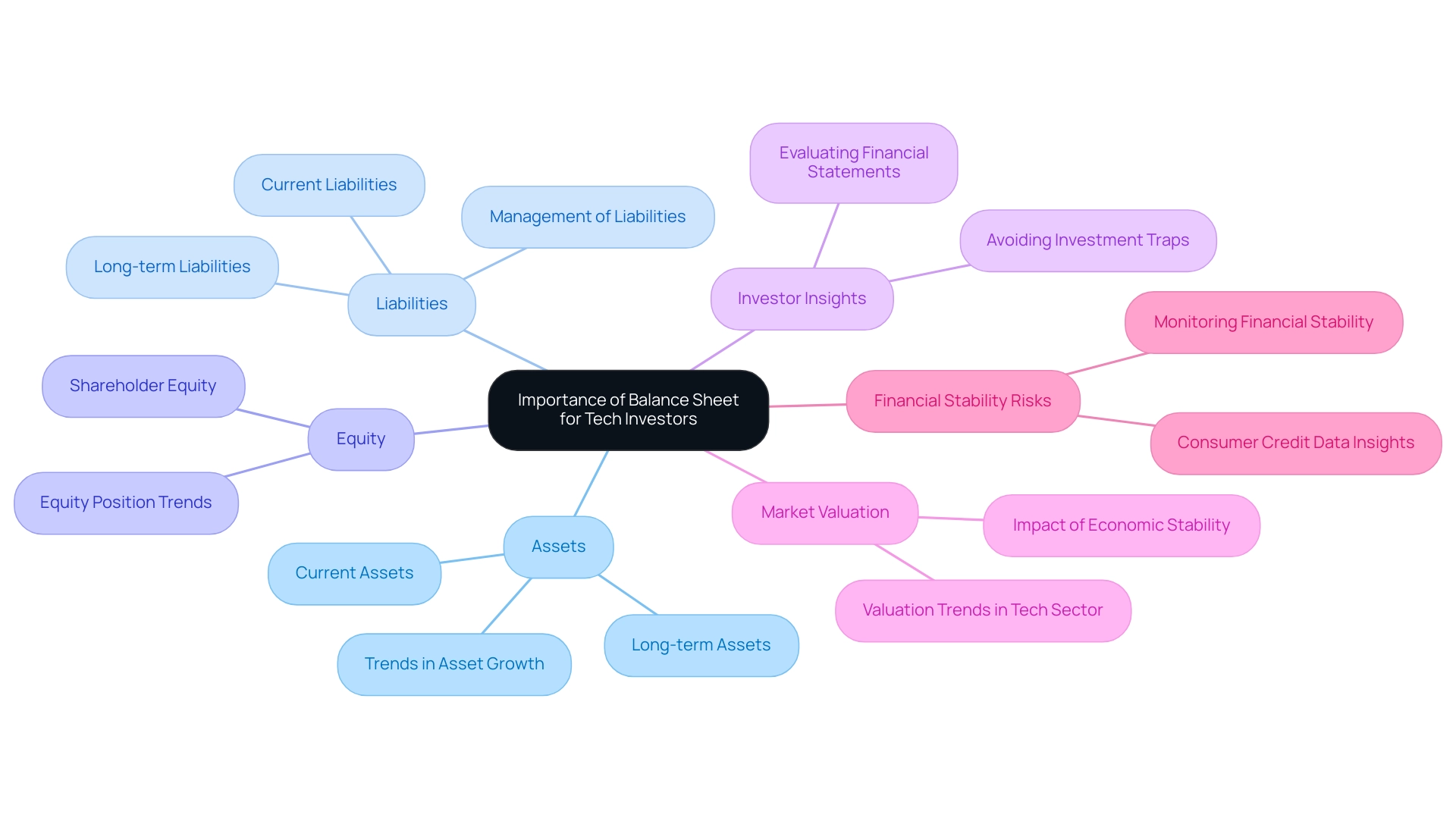
For technology investors, a statement of assets and liabilities is a crucial instrument for evaluating the economic well-being of firms. It provides a clear snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity, allowing investors to evaluate its ability to meet short-term obligations. This assessment becomes increasingly crucial in the dynamic tech sector, where economic stability can drastically influence growth potential and market valuation.
By understanding how to make a balance sheet, investors can identify trends in asset growth, the management of liabilities, and overall equity position. Such insights are critical, especially considering that the major UK banks and building societies represent approximately 75% of lending to the real economy, indicating a strong economic backdrop for investment. The UK banking system's resilience, marked by substantial levels of capital and liquidity, strengthens this stability; major banks have shown strong asset quality and profitability, enabling them to support businesses, including technology companies, even during challenging economic conditions.
Moreover, as the Financial Policy Committee (FPC) supports the Financial Conduct Authority's (FCA) initiatives for comprehensive consumer credit data, investors can gain deeper insights into financial stability risks within the technology landscape. As stated by investment specialist Jane Doe, 'A thoroughly examined financial statement can uncover a technology firm's genuine potential and assist investors in steering clear of traps.' This thorough examination, backed by real-world instances of technology firms that have made strategic adjustments based on financial assessments, aids in guiding investment choices, ensuring that investors in the technology sector are well-prepared to take advantage of opportunities in an industry marked by swift transformation and possible instability.
Key Components of a Balance Sheet: Assets, Liabilities, and Equity
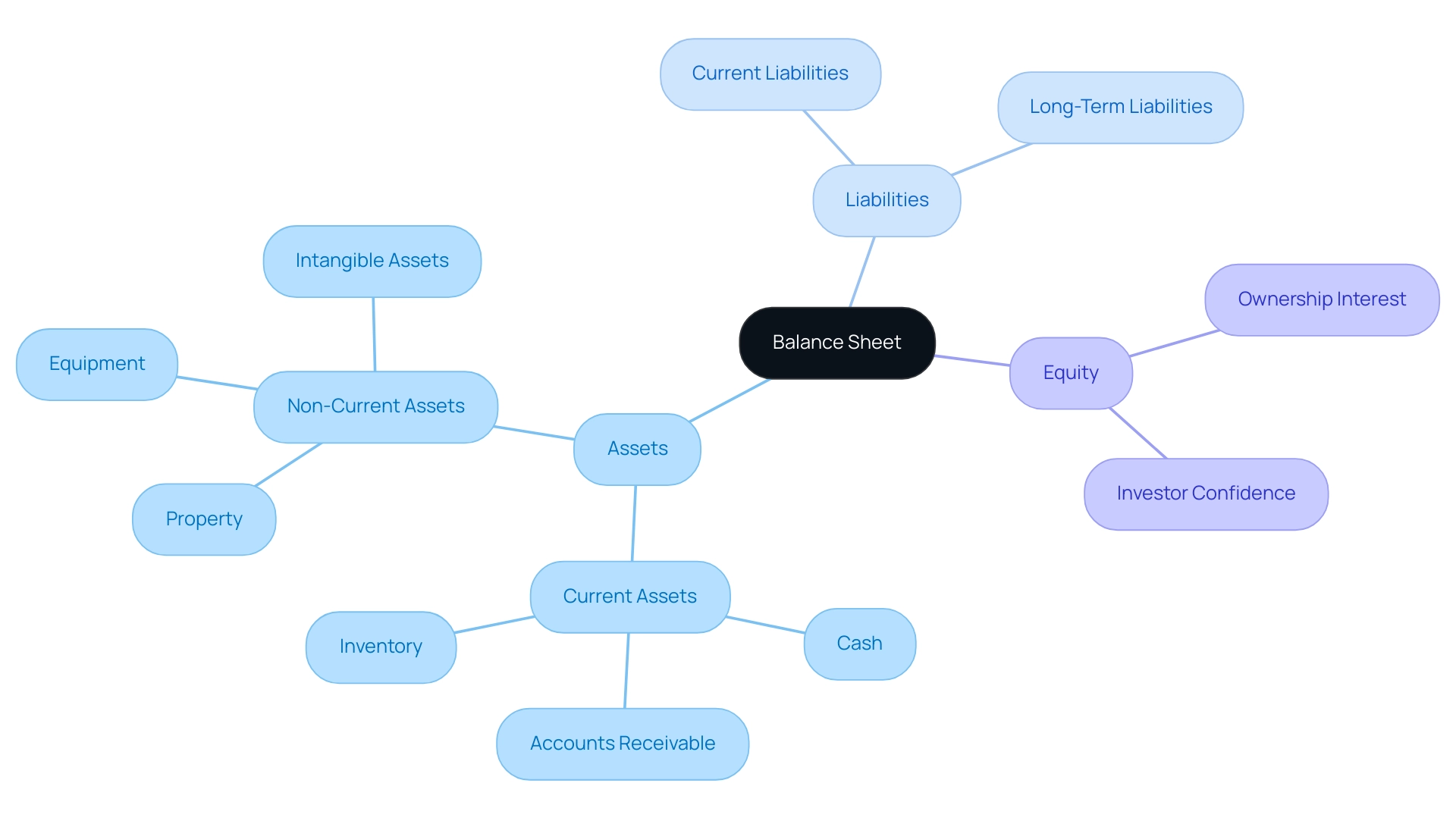
A balance sheet is a fundamental economic statement that explains how to make a balance sheet by including three primary components: assets, liabilities, and equity.
-
Assets: These represent the resources owned by a company, which can be categorized into current assets—such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory—and non-current assets, including property, equipment, and intangible assets.
Grasping the asset composition is essential for investors, especially in the technology sector, where the average asset composition in technology firms is expected to change considerably in 2024. This knowledge enables stakeholders to assess a company's operational efficiency and liquidity, especially as the efficiencies gained through AI are projected to enhance customer experiences and drive cost savings by 2025. Notably, U.S. government spending in AI, ML, and autonomy has increased significantly from 2018 to 2023, reflecting the growing importance of these technologies in various sectors.
-
Liabilities: These are the obligations that a company owes to external parties and can be classified as current liabilities (due within one year) or long-term liabilities (due after one year). Analyzing a company's liabilities is essential for understanding how to make a balance sheet that accurately reflects its debt levels and financial risk. Recent statistics indicate a rising trend in liabilities on balance sheets within the technology sector, reflecting the industry's adaptive strategies in a rapidly changing economic environment.
For instance, asset and wealth management organizations face significant challenges in retiring legacy systems and modernizing their technological infrastructure, which can lead to increased liabilities if not managed effectively.
-
Equity: This component signifies the residual interest in the company's assets after all liabilities have been deducted. It signifies the ownership interest held by shareholders and acts as a barometer for economic health and investor confidence.
A robust equity position not only signals stability but also fosters greater trust among investors, which is crucial in today's competitive landscape. The AI @ Morgan Stanley Debrief tool exemplifies how AI is being utilized in financial advisory, allowing financial advisers to capture and aggregate insights from client conversations to generate personalized recommendations and outline the next steps, thereby enhancing the relevance of AI in the context of financial statements.
Through a detailed examination of these components, tech investors can derive valuable insights into how to make a balance sheet that accurately represents a company's financial structure and risk profile, particularly in light of the challenges faced by asset and wealth management organizations in modernizing their tech infrastructure. Such understanding is vital, especially as firms aim to integrate new technologies while managing legacy systems effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your Balance Sheet
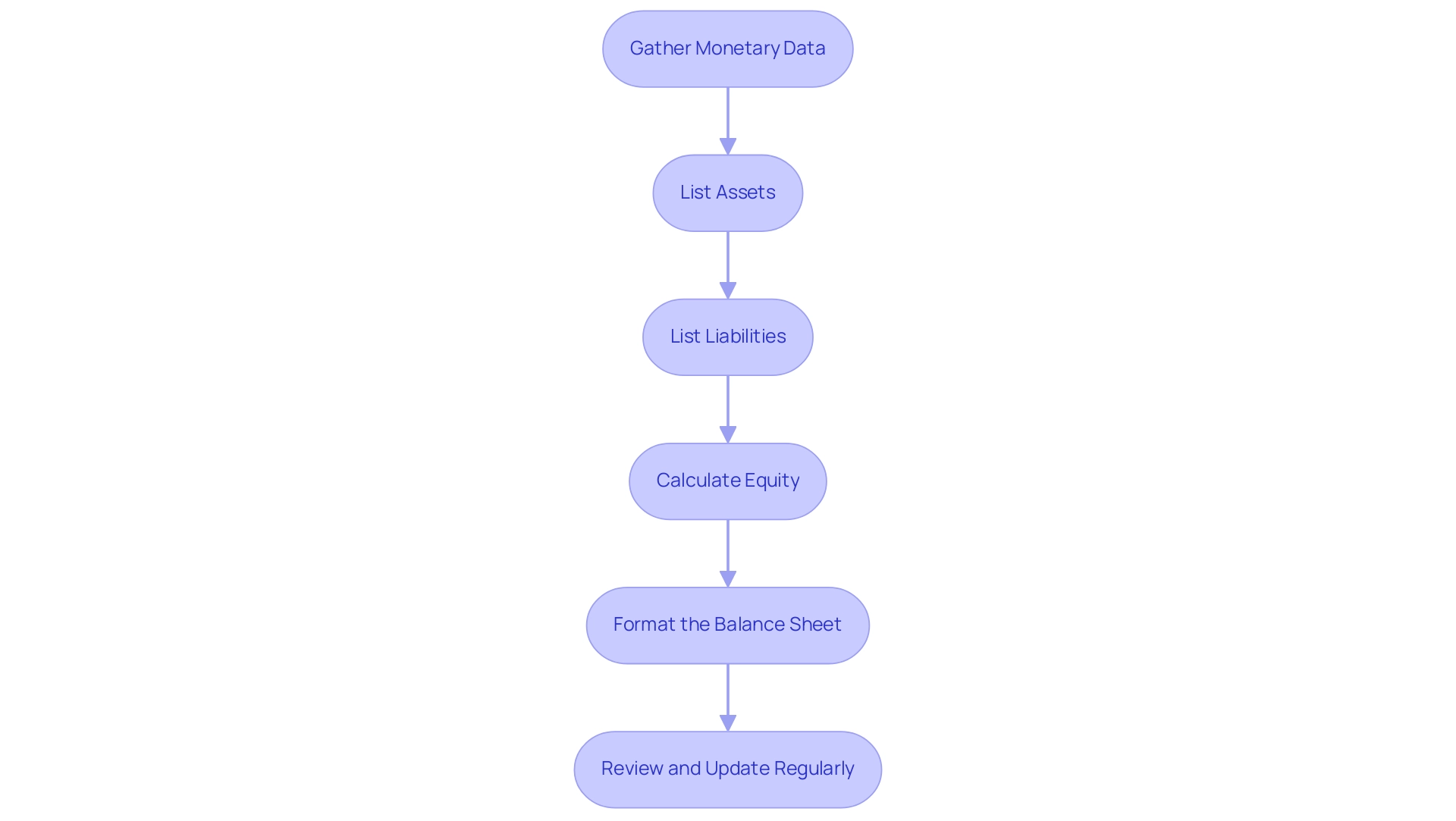
Developing a financial statement is a methodical procedure that includes multiple essential stages to guarantee precision and adherence to best practices. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to make a balance sheet effectively:
-
Gather Monetary Data: Start by collecting all pertinent monetary information, including bank statements, invoices, and records of both assets and liabilities.
This foundational step is crucial, as it provides a comprehensive view of your monetary status.
-
List Assets: Next, categorize and list all assets owned. Begin with current assets, such as cash or accounts receivable, followed by non-current assets like property and equipment.
Assign values based on market rates or book value to ensure an accurate representation. Notably, a retail company’s high return on assets ratio can suggest effective use of assets to generate profits, which is an important consideration in your asset management strategy.
-
List Liabilities: Document all outstanding debts and obligations, classifying them into current liabilities (due within one year) and long-term liabilities.
This should encompass loans, accounts payable, and any other monetary obligations to provide a clear picture of your commitments.
-
Calculate Equity: Determine your equity position by applying the formula:
Equity = Total Assets - Total LiabilitiesThis calculation reflects your net worth and is essential for evaluating the economic health of your business.
-
Format the Balance Sheet: This guide will show you how to make a balance sheet by organizing the information into a structured format, ensuring that assets are displayed on one side and liabilities plus equity are detailed on the opposite side.
It’s essential that both sides are equal, confirming the equation:
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Equity -
Review and Update Regularly: A statement should be regarded as a dynamic document, revised frequently to precisely represent any alterations in your economic situation.
This practice not only helps in maintaining precise records but also aligns with the latest trends in management, such as those observed in 2024.
Incorporating tools like ClickUp can streamline this process, assisting businesses in staying organized and meeting reporting deadlines efficiently. For instance, transitioning to Ramp for Bill Pay has saved companies around $40,000 annually, highlighting the economic advantages of employing the appropriate tools in preparing accounts.
Moreover, as the industry progresses, embracing best practices that acknowledge the intricacies of data visualization—such as knowing your audience and maintaining clarity—will improve the effectiveness of your report.
As emphasized by finance experts, this foundational document is not merely a snapshot of your economic health; it serves as a vital tool for strategic planning and investment decisions.
Furthermore, the case study 'How to Prepare a Financial Statement' demonstrates that crafting a financial statement can be made easier with the appropriate method and resources, highlighting the significance of setting a reporting date and time frame.
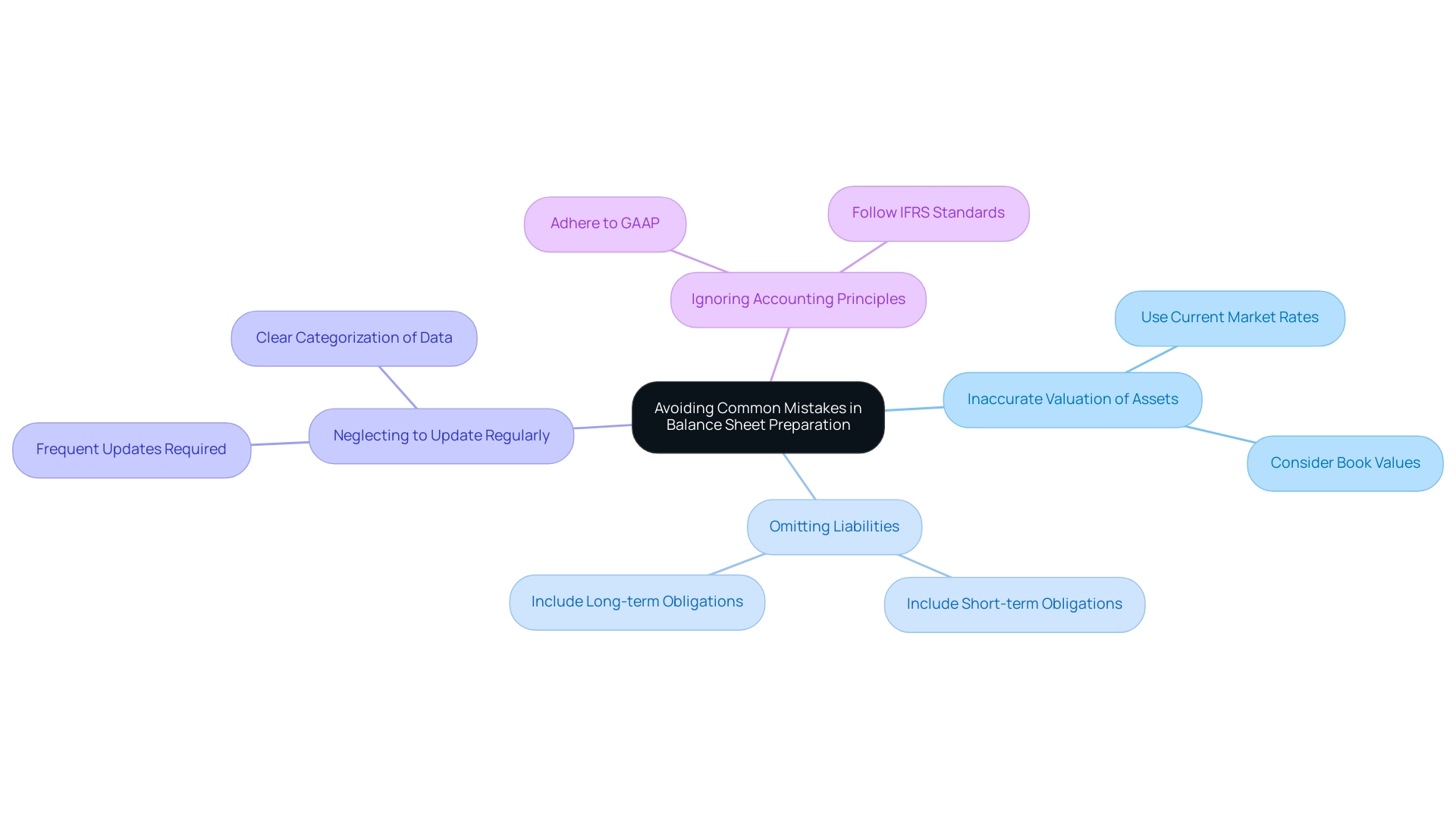
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Balance Sheet Preparation
When creating a statement of position, tech investors must be attentive to several common errors that can greatly influence reporting of accounts:
- Inaccurate Valuation of Assets: Accurate asset valuation is crucial. Utilize current market rates or book values to avoid misrepresenting economic health. A misstep here can lead to significant discrepancies in reported equity.
- Omitting Liabilities: It’s essential to include all obligations in the financial statement. Neglecting to consider short-term and long-term obligations can lead to an exaggerated perception of equity, deceiving stakeholders about the actual economic position of the business.
- Neglecting to Update Regularly: A financial statement must represent the most current monetary condition of the company. Frequent updates are essential; without them, the financial statement can swiftly become obsolete and less helpful for decision-making. Improper formatting can impact how to make a balance sheet, which is essential for organization. Clear categorization of assets, liabilities, and equity is important for understanding how to make a balance sheet and helps prevent confusion and misinterpretation of the data. A disorganized statement might lead investors to draw incorrect conclusions.
- Ignoring Accounting Principles: Adherence to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is critical for ensuring compliance and reliability. Neglecting these standards can lead to significant errors and undermine the credibility of monetary reporting.
The importance of understanding these aspects is underscored by the fact that 59% of accountants report making multiple errors each month, often due to the pressures of economic volatility, with 82% stating that such volatility has increased demands for their work. Additionally, many analysts overlook the reflexivity and interactivity among the three major economic statements, which can conceal inconsistencies and potential fraud. For instance, in one case, an analyst identified a significant mismatch in operating cash flows by recognizing how interconnected statements are, illustrating the necessity of thorough analysis.
Moreover, the return on precious metals and the examination of net write-offs are essential elements that can affect financial accuracy and must not be neglected. As noted by Nicholas Warren, CFA,
Many thanks, Jason, that was a really valuable article and much appreciated,
emphasizing the significance of accurate reporting in fostering investor trust and delivering dependable insights.
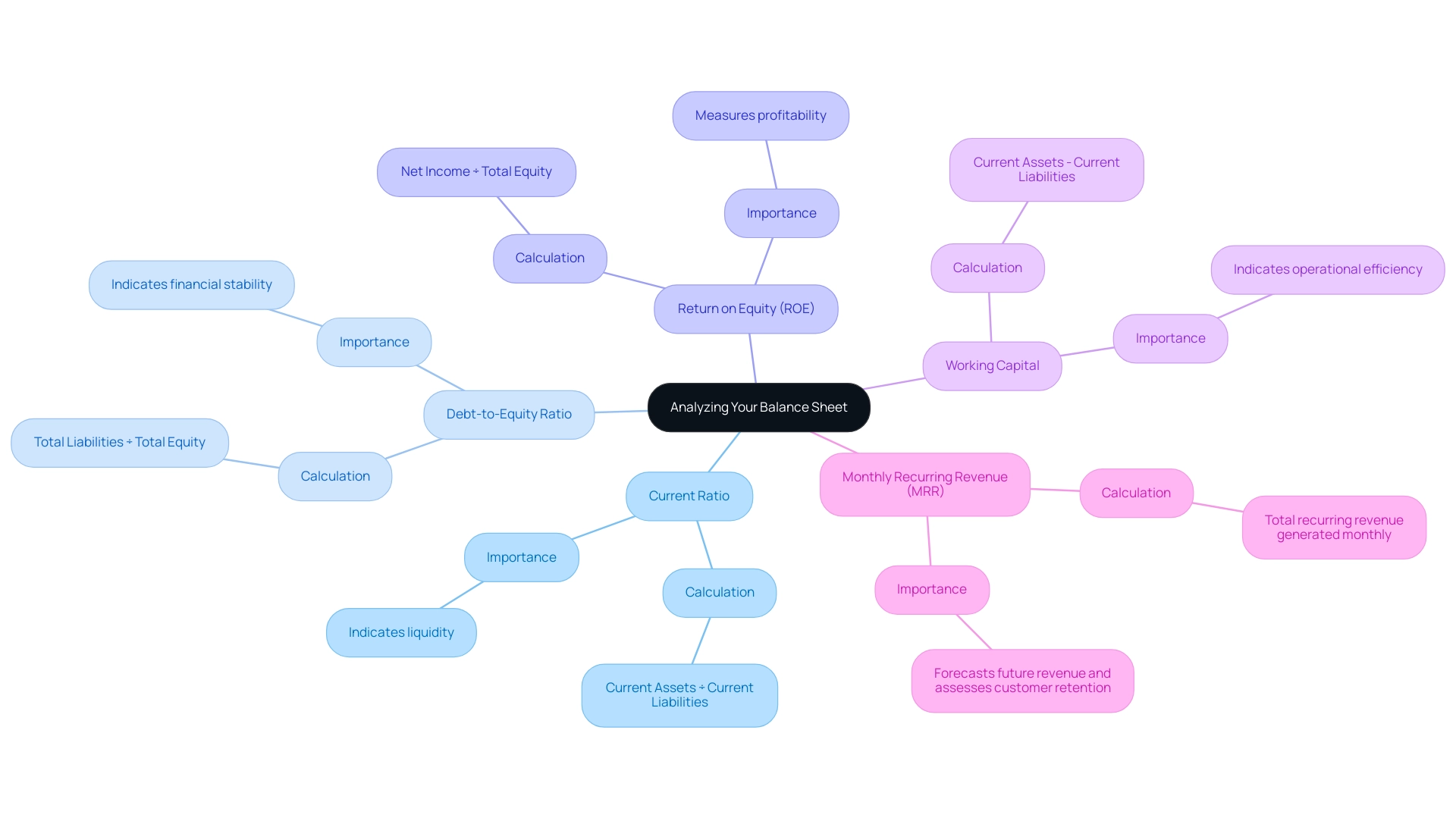
Analyzing Your Balance Sheet: Key Ratios for Tech Investors
Understanding how to make a balance sheet is crucial for technology investors, as it involves calculating key financial ratios that reveal a company's financial health and operational efficiency. Here’s a closer look at some essential ratios:
-
Current Ratio: This ratio assesses a company's capability to meet short-term obligations with its current assets.
It is calculated as Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities. A ratio exceeding 1 is generally considered indicative of strong liquidity. This is particularly important in the technology sector, where maintaining liquidity can be vital for growth and stability, especially for startups.
Since technology companies typically have low inventory levels, the cash ratio is a more accurate test of their ability to pay short-term debts, further emphasizing the importance of liquidity management.
-
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This metric assesses a company's leverage by comparing total liabilities to shareholders' equity.
It is calculated as Total Liabilities ÷ Total Equity. A lower ratio indicates a more financially stable company, which is crucial for technology firms seeking to attract investors. As emphasized by industry trends, Molson Coors Beverage Co. intends to lower its leverage ratio to under 3 times, indicating a wider shift towards economic caution that technology firms are also embracing to boost investor confidence.
-
Return on Equity (ROE): This ratio measures how effectively a company utilizes equity to generate profits, calculated as Net Income ÷ Total Equity.
Higher ROE values indicate improved economic performance, making this a key indicator for technology investors evaluating the profitability of their investments.
-
Working Capital: This metric indicates the difference between current assets and current liabilities and is calculated as Current Assets - Current Liabilities.
Positive working capital is essential for operational efficiency and suggests that a company can fund its day-to-day operations comfortably.
Additionally, the Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) metric is vital for SaaS companies, capturing the total recurring revenue generated monthly.
This metric not only assists in predicting future revenue but also in assessing customer acquisition and retention strategies, thus offering insights into a company's economic health.
By understanding how to make a balance sheet and analyzing these ratios, investors in technology can gain a comprehensive view of a company's fiscal position, empowering them to make informed investment decisions. As Brianna Blaney emphasizes, combining ratio analysis with cash flow and profitability assessments provides a holistic view of performance, aligning well with today’s trends in automation.
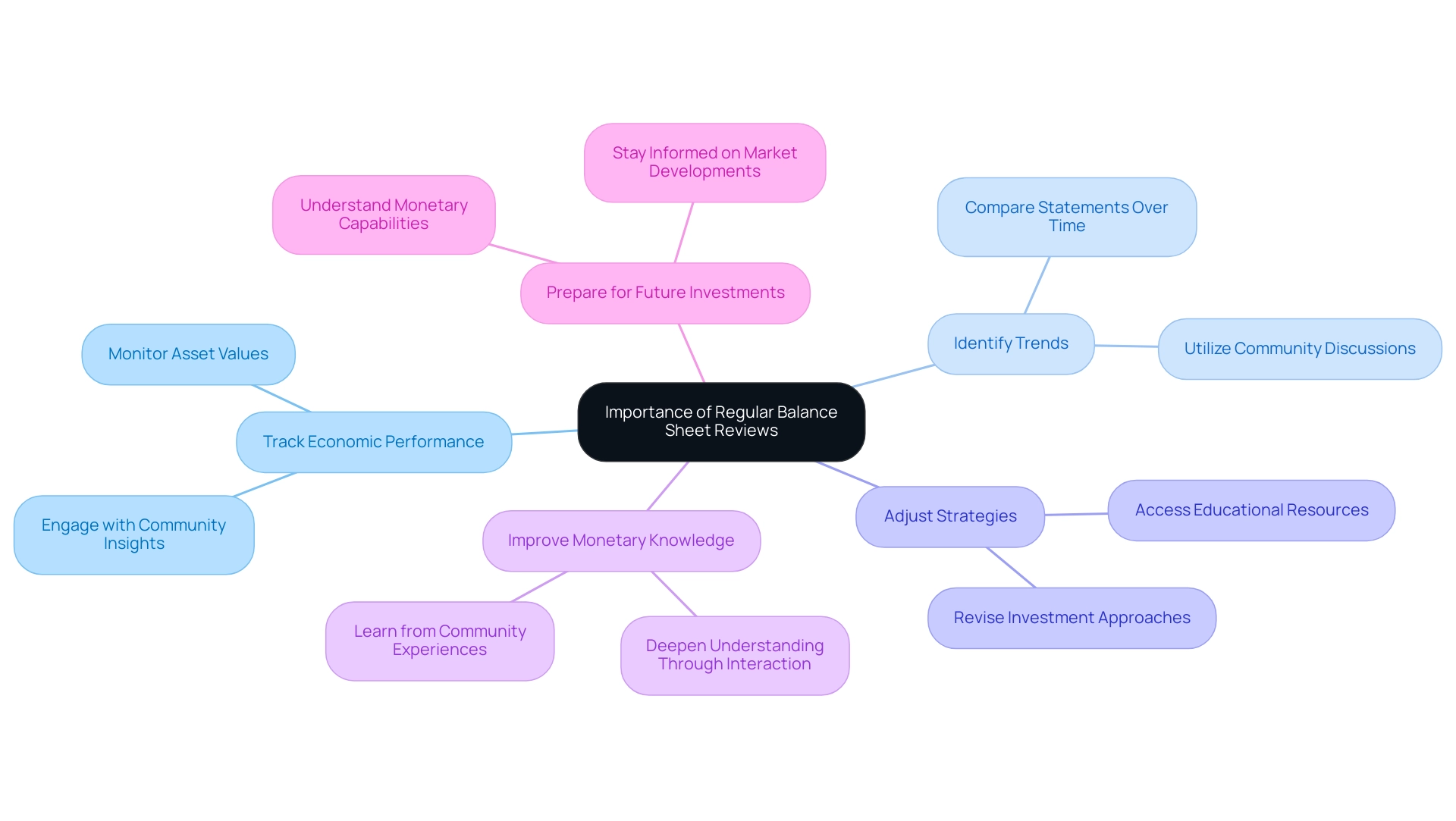
The Importance of Regular Balance Sheet Reviews
Consistently assessing your statement of assets and liabilities is crucial for acquiring a thorough insight into your monetary status, particularly for tech investors interacting with the community at fff.club, which has more than 400 members. Here are several reasons why this practice is invaluable:
-
Track Economic Performance: Frequent reviews allow you to closely monitor fluctuations in asset values, liabilities, and equity, providing you critical insights into your economic performance over time.
Engaging with over 400 members of the fff.club community can provide additional perspectives on market trends and investment strategies.
-
Identify Trends: By comparing statements of assets and liabilities across different periods, you can pinpoint patterns that reflect your economic well-being.
This trend analysis is particularly relevant for tech investors, who can use insights gained from community discussions to inform their investment decisions.
-
Adjust Strategies: Regular revisions to your accounts enable you to alter your investment approaches in reaction to shifts in your economic situation and existing market conditions.
The educational resources available through fff.club can support these adjustments by keeping you informed on best practices and emerging opportunities.
-
Improve Monetary Knowledge: Interacting frequently with your account statement encourages deeper monetary understanding.
By participating in the fff.club community, you gain access to exclusive investment opportunities and insights that equip you with the knowledge to make more informed investment choices.
For instance, community members often share their experiences and strategies, enriching the learning environment.
-
Prepare for Future Investments: Understanding how to make a balance sheet positions you well for future investment opportunities, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of your monetary capabilities.
The weekly summary of economic, monetary, and technological developments shared with fff.club members further enhances your preparedness for upcoming ventures, including exclusive opportunities that arise within the community.
The Financial Policy Committee (FPC) emphasizes the significance of maintaining a stable economic environment, stating,
The FPC is maintaining the UK countercyclical capital buffer (CcyB) rate at its neutral setting of 2%
which underscores the need for businesses and investors to be vigilant about their economic metrics.
Additionally, as the net external assets of euro area MFIs increased by €553 billion in 2024, it highlights the shifting economic landscape that tech investors must navigate.
The statement not only represents your economic position but also the total net worth of the UK, making it an essential tool for understanding wider economic conditions.
Moreover, the recent case study on the Countercyclical Capital Buffer Rate Decision demonstrates how the FPC's choices affect financial stability and, in turn, asset management.
By committing to regular balance sheet reviews and understanding how to make a balance sheet with the community resources at fff.club, tech investors can ensure they remain informed and proactive in their investment strategies, ultimately enhancing their decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering the balance sheet is essential for tech investors navigating today's complex financial landscape. This article has emphasized the balance sheet's role as a critical financial statement, providing a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. By analyzing these components, investors can assess a company's fiscal health and make informed decisions, particularly in light of improving corporate resilience and lower net debt to earnings ratios.
Key insights from the article highlight the importance of:
- Accurate asset valuation
- Comprehensive liability documentation
- Regular updates to balance sheets
Avoiding common pitfalls such as omitting liabilities or neglecting to adhere to accounting principles is crucial to maintain the integrity of financial reporting. Moreover, understanding key financial ratios—like the current ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on equity—enables investors to evaluate a company's operational efficiency and financial stability effectively.
Regular reviews of balance sheets not only enhance financial literacy but also empower tech investors to adjust strategies based on market conditions and company performance. Engaging with community resources and discussions can further enrich this understanding, providing diverse insights and fostering informed investment choices.
Ultimately, the balance sheet serves as more than just a financial document; it is a strategic tool that can significantly influence investment outcomes. By leveraging the insights and guidelines discussed, tech investors can position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving market, ensuring they remain agile and well-informed in their investment strategies.



