Overview
Bootstrapping for startups involves self-funding techniques that allow entrepreneurs to finance their ventures through personal savings and generated revenue, enabling them to maintain control and promote financial discipline. The article highlights that successful bootstrapping fosters innovation and resilience, as evidenced by notable companies like Mailchimp and Basecamp, which have thrived without external investment by focusing on profitability and sustainable growth.
Introduction
In a world where external funding often reigns supreme, the art of bootstrapping emerges as a powerful alternative for aspiring entrepreneurs. This self-funding strategy not only fosters complete control over business decisions but also cultivates a culture of resourcefulness and innovation.
With the rise of successful self-funded companies, such as Mailchimp and Basecamp, bootstrapping is gaining recognition as a viable path to sustainable growth. Yet, while the benefits are enticing, the journey is fraught with challenges, from limited resources to the pressure of personal financial risk.
This article delves into the fundamentals of bootstrapping, exploring its advantages, potential pitfalls, effective strategies, and the importance of community support, ultimately illuminating how entrepreneurs can thrive in a competitive landscape without relying on outside investors.
Understanding Bootstrapping: The Basics of Self-Funding
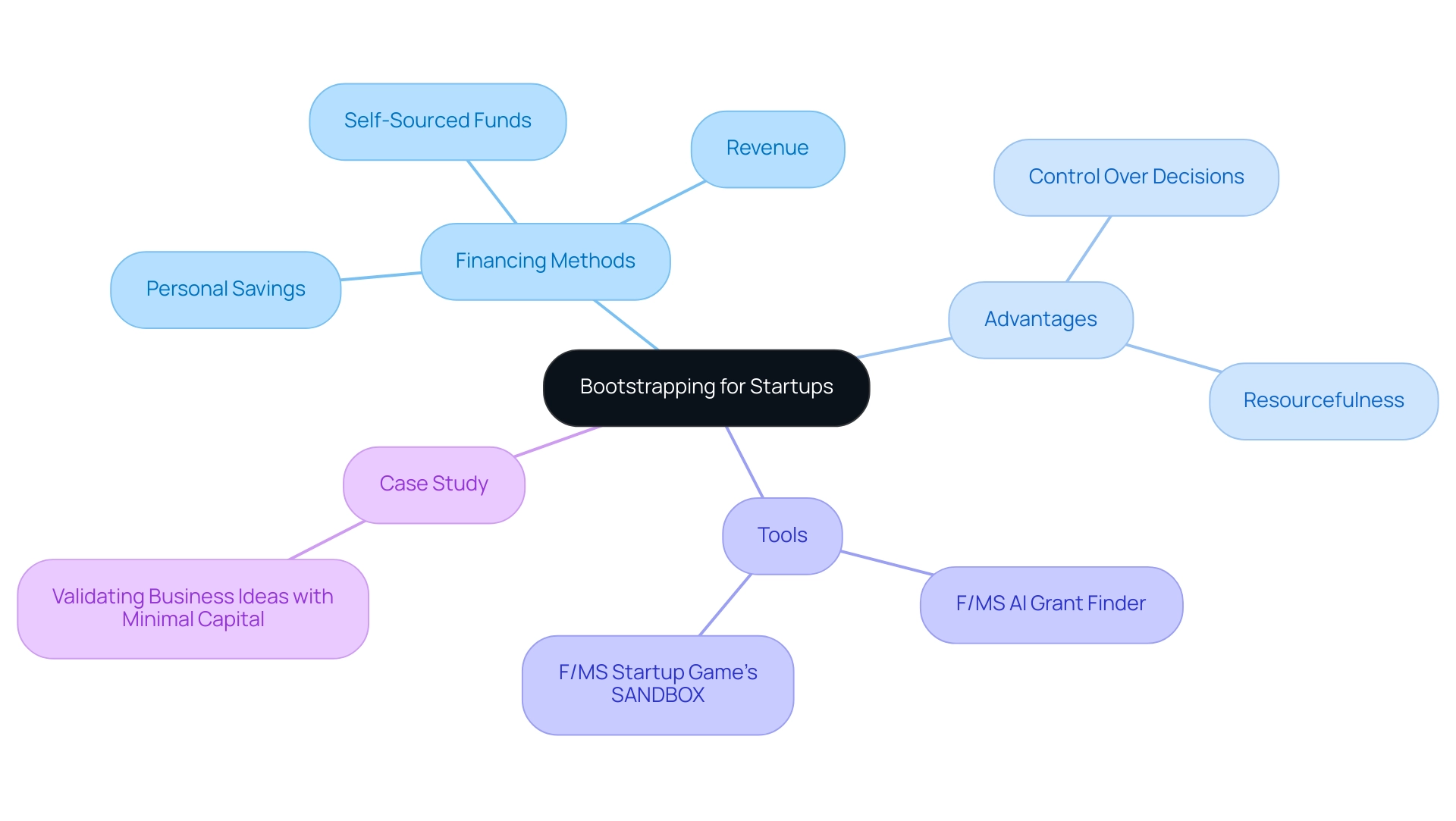
Bootstrapping for startups refers to the strategy of financing a new venture through personal savings, revenue generated by the enterprise, or other self-sourced funds, rather than relying on external investments. This approach empowers business owners to retain complete control over their decisions and strategic direction by utilizing bootstrapping for startups. By adhering to a lean startup model, bootstrapping for startups means allocating every dollar judiciously, focusing on maximizing growth while minimizing unnecessary expenditures.
This financial discipline fosters a culture of resourcefulness and innovation, compelling entrepreneurs to creatively address challenges within their constraints by embracing bootstrapping for startups. As of 2023, there are over 1,200 unicorns worldwide, many of which originated from self-funded beginnings, illustrating the potential of bootstrapping for startups as a route to success. Entrepreneurs can further enhance their bootstrapping efforts by utilizing tools like the F/MS AI Grant Finder, which assists in identifying suitable EU grants and aids in application drafting.
Additionally, the case study 'Validating Business Ideas with Minimal Capital' demonstrates how creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) can test market demand without significant investment, allowing business owners to gather feedback from initial customers. Using tools like F/MS Startup Game's SANDBOX for AI simulations can help stress-test models, potentially reducing failure rates.
The Advantages of Bootstrapping: Why Choose Self-Funding?
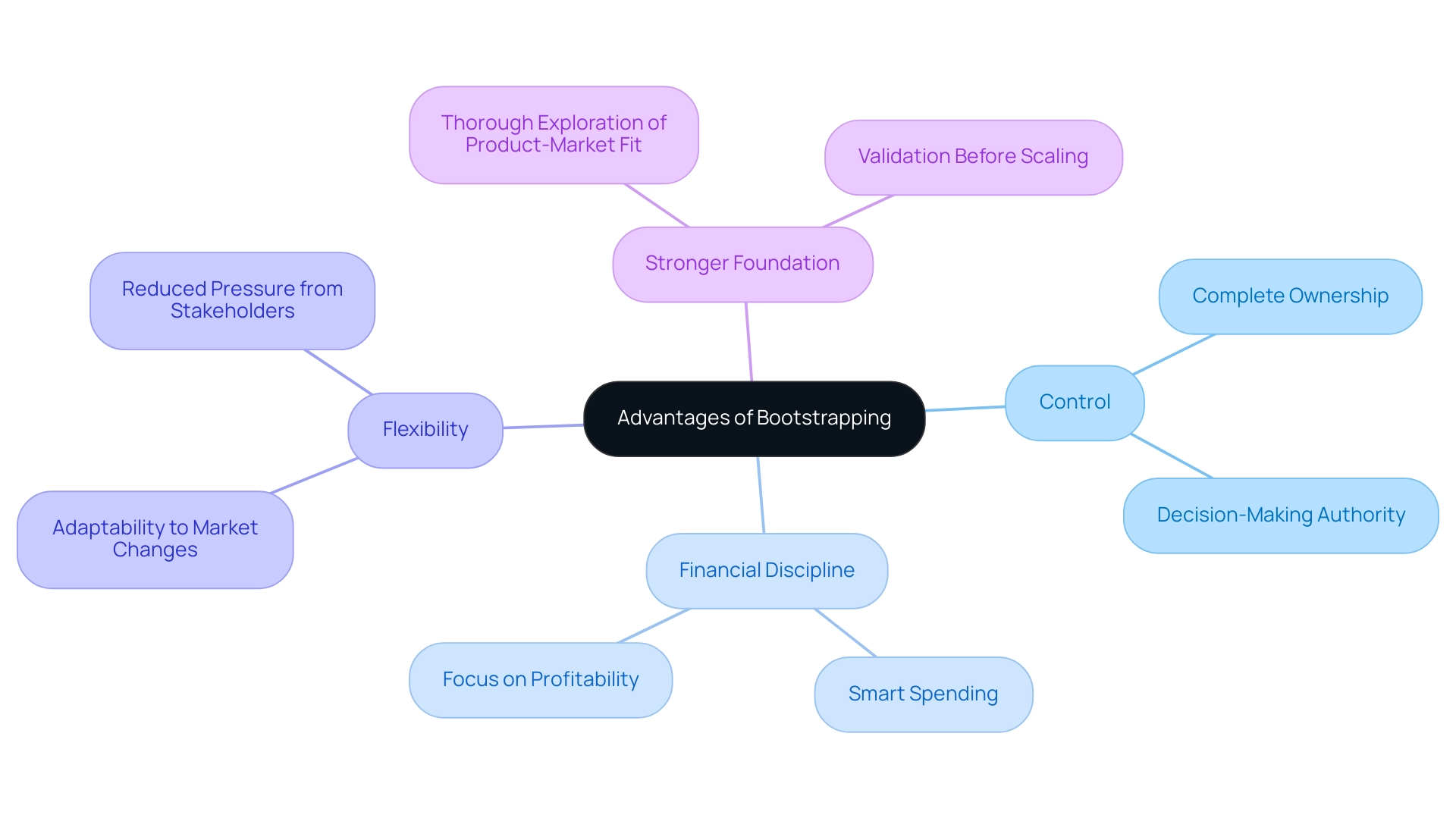
Bootstrapping for startups provides numerous benefits for entrepreneurs aiming to launch their ventures. Key benefits include:
- Control: Founders maintain complete ownership and decision-making authority, enabling them to navigate the company’s direction without external investor interference. This autonomy allows for a more personalized vision and strategy.
- Financial Discipline: Operating under constrained financial resources fosters a focus on profitability and sustainability. Entrepreneurs are compelled to prioritize smart spending, which in turn promotes strategic growth and long-term viability.
- Flexibility: The absence of external stakeholders alleviates pressure, allowing bootstrapped startups to pivot and refine their models as market conditions change. This adaptability is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving landscape.
- Stronger Foundation: Establishing an enterprise without dependence on external funding often necessitates a thorough exploration of product-market fit. This rigorous approach establishes a more resilient company, as entrepreneurs must validate their concepts before scaling.
Moreover, the technique can be likened to the statistical method of resampling, where original datasets are reused to create simulated datasets. This analogy highlights the effectiveness of bootstrapping as it encourages new ventures to repeatedly test and refine their business ideas, much like how bootstrapping in statistics provides robust inference when sample sizes are insufficient.
As Jim wisely points out, "I believe it will be clearer after reading the post I link to above," highlighting that deeper insights into these strategies can yield significant benefits for aspiring business owners. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Sample Size Considerations for Bootstrapping' illustrates the significance of meticulous planning in bootstrapped businesses, urging individuals to consider various factors influencing their sample size and representation, ultimately resulting in more informed decision-making.
By embracing bootstrapping, new ventures can cultivate a culture of financial discipline that not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions them for sustainable growth.
Navigating the Challenges: The Risks of Bootstrapping
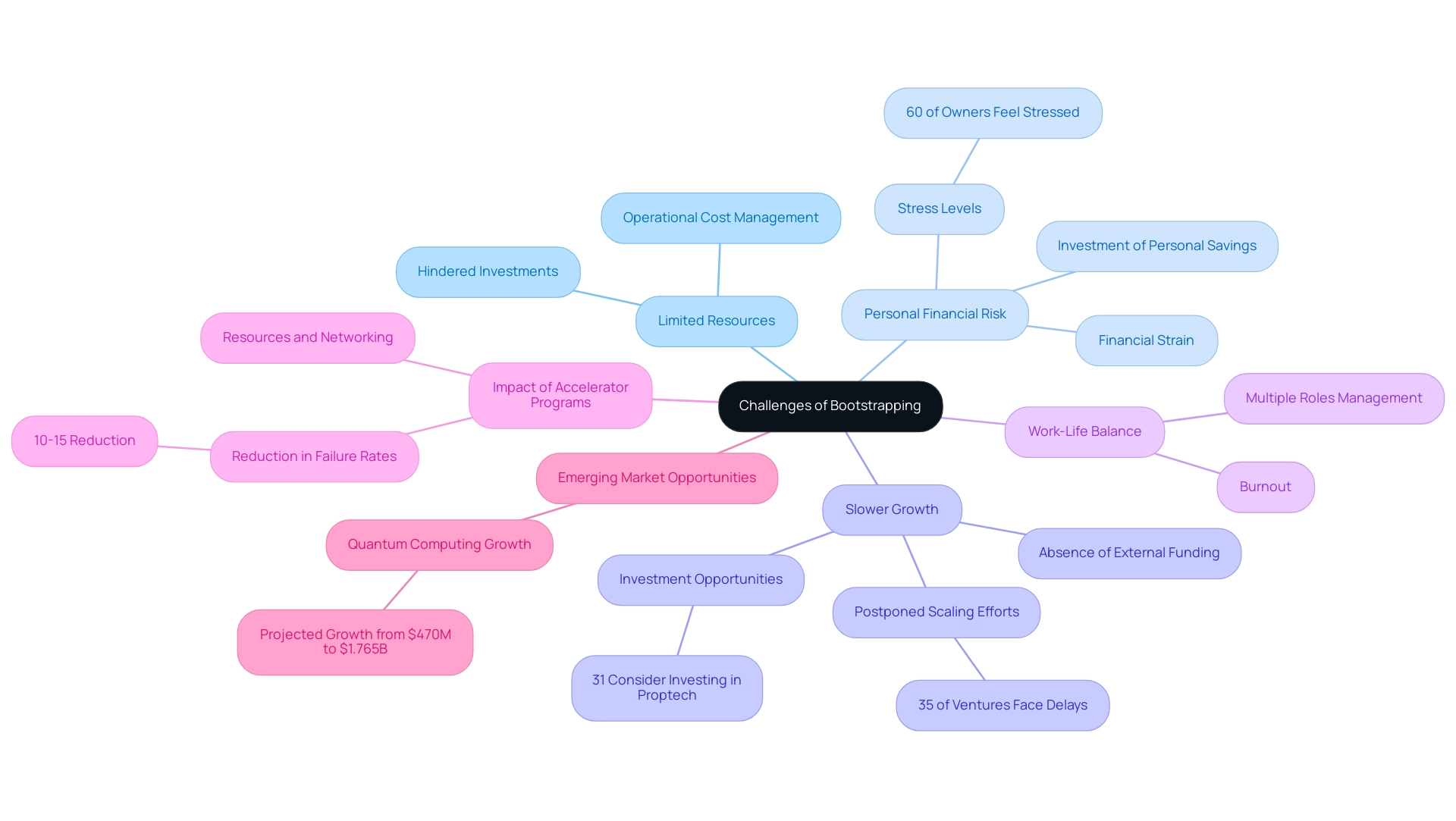
Bootstrapping a new business can offer substantial independence and authority, yet it introduces a distinct array of challenges that business owners must navigate:
- Limited Resources: Many new ventures face the daunting task of managing operational costs with restricted finances. Insufficient capital can hinder essential investments in technology, marketing, and hiring, ultimately stifling growth and innovation.
- Personal Financial Risk: A substantial number of business owners invest their personal savings into their ventures, exposing themselves to significant financial strain. This risk can lead to personal hardships, especially if the venture fails to achieve profitability. Recent statistics indicate that nearly 60% of business owners report feeling stressed about their financial investments in their ventures, highlighting the weight of this burden.
- Slower Growth: The absence of external funding can result in a slower growth trajectory, allowing competitors to potentially outpace self-funded businesses. Without the capability to expand rapidly, companies may forfeit crucial market opportunities, with approximately 35% of self-funded ventures facing postponed scaling efforts. Notably, the investment landscape shows that approximately 31% of United States-based commercial investors consider investing in proptech companies, which could represent an opportunity for tech-focused self-funded ventures.
- Work-Life Balance: Self-funded founders often juggle multiple roles within their businesses, leading to an imbalance that can foster burnout. The demands of managing a fledgling business typically require extended hours, which can strain personal relationships and overall well-being.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for entrepreneurs considering bootstrapping for startups. As highlighted by the Harvard Business Review, the effectiveness of accelerator programs can mitigate some risks, with participation associated with a 10-15% reduction in failure rates. By utilizing resources, guidance, and networking opportunities, new ventures can more effectively manage the challenges of self-funding.
Furthermore, emerging sectors such as quantum computing, projected to grow from $470 million in 2021 to $1,765 million by 2026, present additional opportunities for self-funded ventures to innovate and capture market share.
Effective Bootstrapping Techniques: Strategies for Success
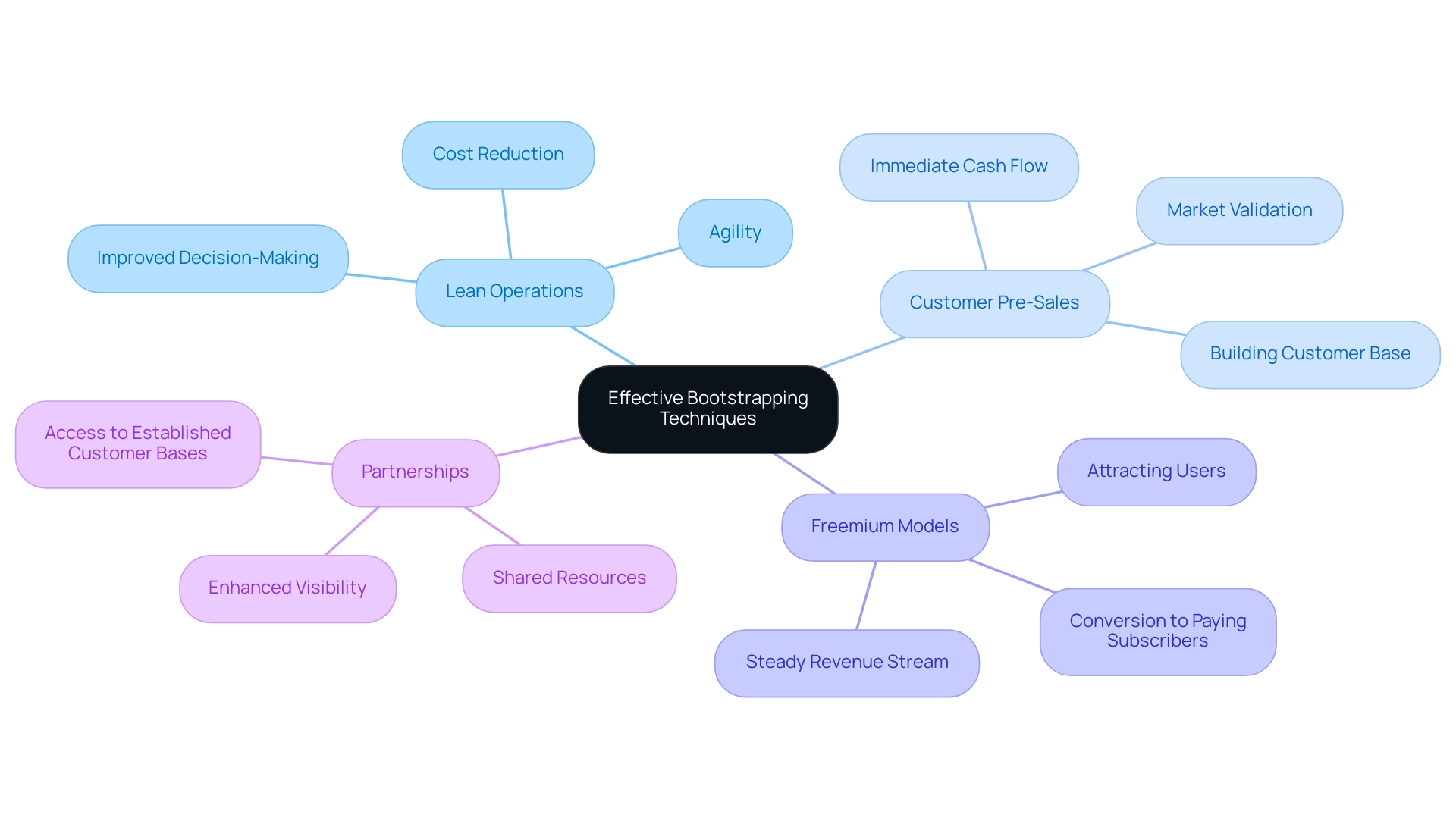
Several effective bootstrapping techniques can significantly enhance the success of early-stage startups:
-
Lean Operations: Embracing a minimalistic approach allows startups to concentrate on core functions while eliminating unnecessary expenses. This strategy not only reduces operational costs but also fosters agility, enabling quick pivots based on market feedback. As data availability expands, mastering lean operations becomes crucial for improving accuracy in analysis and decision-making.
-
Customer Pre-Sales: Validating your business concept through customer pre-sales can yield immediate cash flow to support further development. This strategy not only tests the market's response but also builds a committed customer base before the product is fully developed. Research indicates that new ventures employing this technique see higher success rates, as it aligns product offerings with actual market demand.
-
Freemium Models: By offering a free version of a product or service, companies can attract a larger user base. This approach creates opportunities to convert a fraction of free users into paying subscribers, generating a steady revenue stream. The effectiveness of freemium models has been widely acknowledged, with many successful companies leveraging this strategy for growth.
-
Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses can lead to shared resources and reduced operational costs. Such partnerships often enhance visibility and market reach, allowing new businesses to tap into established customer bases. As Saurav Das emphasizes,
This distribution then helps you estimate standard errors, confidence intervals, and other measures of uncertainty <—a critical factor when assessing the potential success of collaborative ventures.
In the context of resampling, it is recommended to utilize between 1,000 and 10,000 bootstrap samples for reliable results, reinforcing the importance of data-driven decision-making. Furthermore, the case study named 'Bootstrapping Resampling Process' demonstrates the practical use of resampling techniques in new businesses, where sampling the original dataset with replacement generates simulated datasets, offering a distribution of sample statistics crucial for estimating the sampling distribution.
These methods, supported by a strong grasp of efficient self-funding practices, will be essential for bootstrapping for startups as new ventures maneuver through the intricacies of the 2024 market environment.
Success Stories: Companies That Thrived Through Bootstrapping
The landscape of entrepreneurship is filled with compelling success stories of companies that have thrived through self-funding, highlighting the effectiveness of bootstrapping for startups. Notable examples include:
- Mailchimp: Initially conceived as a side project, Mailchimp evolved into a leading email marketing platform that achieved remarkable success without seeking outside investment. By prioritizing profitability from its early stages, Mailchimp demonstrated that a disciplined approach to finances can lead to sustainable growth and market leadership.
- Basecamp: Renowned for its project management software, Basecamp has remained bootstrapped since its inception, focusing on sustainable growth and cultivating a strong company culture. This commitment to self-reliance has allowed Basecamp to navigate the challenges of the tech landscape while maintaining its core values.
- Balsamiq: This innovative wireframing tool company has succeeded by placing a premium on customer feedback and operating with a lean structure. By relying on generated revenues for funding its growth, Balsamiq exemplifies how prioritizing customer needs can drive a bootstrapped company towards success.
These stories resonate with the growing trend of entrepreneurs opting for bootstrapping as a viable funding strategy, particularly in a climate where venture investments into sectors like FinTech reached $81 billion in 2022. As Alex Kotliarskyi, Co-Founder & CTO of Secta Labs, emphasizes, "You have to get pragmatic. Rely on third-party infrastructure and tools to lighten the load."
This reflects a broader industry inclination towards self-sufficiency and sustainable practices. Moreover, bootstrapping for startups involves adopting a long-term mindset, focusing on slow growth and developing paying customers, which is crucial for achieving lasting success.
Building a Support Network: The Role of Community in Bootstrapping
Establishing a robust support network is vital for the success of self-funded businesses, particularly when it comes to bootstrapping for startups. Community engagement not only enhances organizational resilience but also fosters collaboration and innovation. To cultivate such a network, consider the following strategies:
- Join Local Entrepreneur Groups: Engage actively with local business organizations and incubation centers to forge connections with like-minded individuals who share similar challenges and aspirations.
- Leverage Online Communities: Participate in online forums, social media groups, and professional platforms such as LinkedIn. These digital spaces allow business owners to share experiences, gather insights, and expand their reach.
- Seek Mentorship: Identify mentors with experience in bootstrapping or your specific industry. Their seasoned guidance can be instrumental in navigating the complexities of startup challenges.
- Collaborate with Peers: Form strategic partnerships with fellow entrepreneurs. By sharing resources, knowledge, and customer networks, participants can enhance their growth potential and create synergies that drive mutual success.
A notable statistic emphasizes the importance of community: 98% of community enterprises report positive impacts on community cohesion, with 97% noting a reduction in social isolation. Furthermore, only 7% of community businesses successfully raised income through community shares in the last year, highlighting the challenges faced in this area. However, the Kingston Community Society serves as an inspiring example, having raised £140,000 from 208 community shareholders, demonstrating the potential for successful community engagement.
Such findings illustrate the value of collective efforts in fostering an entrepreneurial ecosystem. Additionally, local business groups are invaluable in providing support and resources, mitigating the isolation that often comes with bootstrapping for startups. As one representative from a sports services consultancy noted, local authorities often hesitate to relinquish assets, fearing criticism, which underscores the need for community-driven initiatives to leverage local knowledge and capabilities.
By actively engaging in these communities, entrepreneurs can not only build successful ventures but also contribute to vibrant, interconnected neighborhoods. In sectors like EdTech and eCommerce, for instance, startups can benefit from tailored community support that addresses specific industry needs, enhancing their chances of success.
Conclusion
Bootstrapping emerges as a compelling strategy for entrepreneurs seeking to maintain control and foster innovation while building their businesses. By utilizing personal savings and revenue generated from operations, bootstrapped startups can cultivate a culture of resourcefulness, discipline, and resilience. The advantages of this approach, including complete ownership, financial prudence, and the ability to adapt quickly to market changes, create a strong foundation for long-term success.
However, the journey of bootstrapping is not without its challenges. Entrepreneurs face:
- Limited resources
- Personal financial risks
- The pressure of slower growth
Understanding these hurdles is crucial for those considering this path, as is the recognition that community support can play a pivotal role in navigating the complexities of self-funding. By leveraging local networks, online communities, and mentorship, bootstrapped entrepreneurs can mitigate risks and enhance their chances of success.
Ultimately, the success stories of companies like Mailchimp and Basecamp serve as powerful testaments to the effectiveness of bootstrapping. These examples illustrate that with a long-term vision and a commitment to sustainable growth, entrepreneurs can thrive without relying on external investments. As the landscape of entrepreneurship continues to evolve, embracing bootstrapping may well be a key to unlocking innovation and achieving lasting impact in a competitive world.



