Overview
Syndicate investment is a collaborative funding model where a group of investors pools resources to support ventures, primarily benefiting startups while minimizing individual risks. The article emphasizes that this approach not only provides access to exclusive deals and portfolio diversification but also fosters strategic guidance for startups, demonstrating its growing popularity and effectiveness in the current funding landscape.
Introduction
Syndicate investment has emerged as a powerful model for both investors and startups, facilitating a collaborative approach to funding that mitigates risk while enhancing opportunities. By pooling resources, investors gain access to exclusive deals and diversified portfolios, while startups benefit from crucial capital and strategic guidance.
This article delves into the intricacies of syndicate investments, exploring their structure, advantages, and the essential steps for forming and managing a syndicate. It also addresses the inherent risks and legal considerations that participants must navigate in this dynamic landscape.
As the trend of collaborative investing continues to grow, understanding the mechanics of syndicate investments becomes increasingly vital for those looking to thrive in the competitive market.
Defining Syndicate Investment: An Overview
Syndicate investment is a structured, collaborative model where a group of backers pools their financial resources to support a single venture, often targeting startups or early-stage companies. This method enables participants to share the risks and benefits related to their assets, enhancing personal financial security. Typically, syndicates are organized under the leadership of a lead investor or syndicate manager, who is responsible for identifying promising opportunities, conducting thorough due diligence, and negotiating favorable terms for the collective group.
In the Baltics, figures like Donatas Keras and Kristjan Tamla illustrate the potential of this model, aiding the expansion of companies through their strategic funding in entities such as Practica Capital and ofTEN. Furthermore, fff. Vc operates within this framework, offering participation with specific fees and sourcing deals from a diverse range of opportunities.
It manages portfolios post-closing by leveraging its network and expertise, ensuring that members receive comprehensive support throughout the funding process. The growing number of active groups in startup funding emphasizes the acknowledgment of the benefits provided by syndicate investment models, particularly in regions like the Baltics where innovation and resilience are crucial. Transactions monitored since 2010 demonstrate the effectiveness of syndicate investment, as shown by Blue Owl's ability to raise over 60% of capital from the largest funds pursuing similar collaborative strategies.
Moreover, the case study titled 'Differentiation Through Scale' illustrates how scaled direct lenders are better positioned for success due to their deep origination capabilities and strong sponsor relationships. In contrast, alerts from CBRE concerning commercial real estate valuations indicate that adaptive financial strategies are essential in today's fluctuating market.
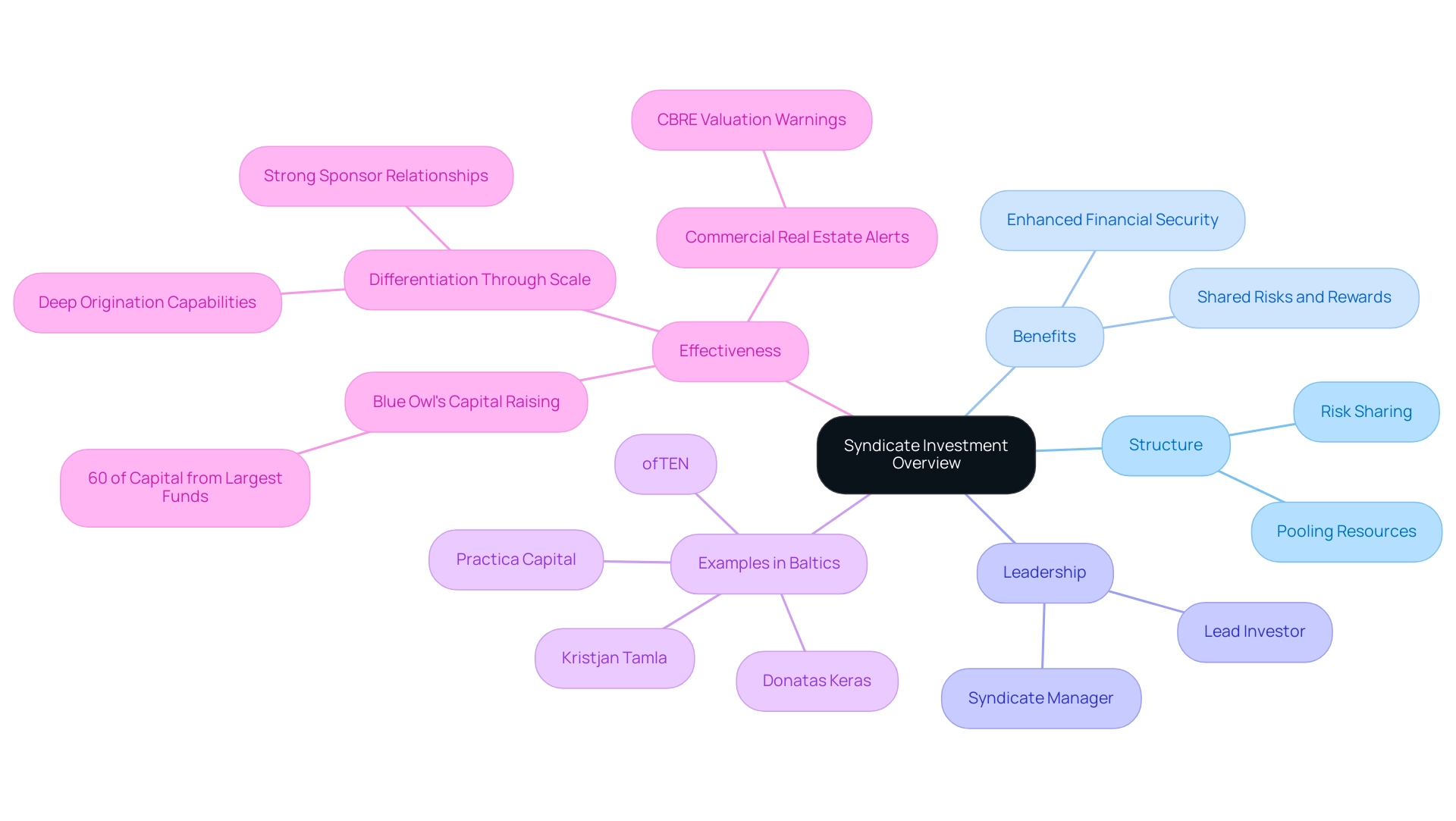
The Benefits of Syndicate Investment for Investors and Startups
Syndicate investment provides numerous benefits for both backers and startups. For stakeholders, these advantages encompass:
- Access to exclusive deals, which are often reserved for larger players in the market
- Decreased individual risk due to the pooling of resources
At fff.club, over 400 tech financiers engage in collaborative investment evaluation and due diligence, leveraging their collective expertise to screen high-grade deal opportunities.
As one stakeholder noted, 'The collaborative approach at fff. Club has opened doors to deals I would never have accessed alone.' This collaborative framework enables investors to learn from seasoned lead investors, allowing for a more informed decision-making process.
Additionally, group contributions enable portfolio diversification, offering chances to participate in high-growth sectors that may otherwise be out of reach. For instance, the global quantum computing market size is projected to grow from $470 million in 2021 to $1,765 million in 2026, emphasizing a profitable sector for funding. For startups, the infusion of capital from group investments is crucial for scaling operations and achieving growth objectives.
Additionally, receiving support from reputable stakeholders lends validation and enhances credibility within the market. Startups also benefit from the strategic guidance provided by group members, fostering an environment conducive to innovation and success. This symbiotic relationship not only nurtures the growth of startups but also fosters satisfaction among financiers, as evidenced by the robust interest in sectors like proptech, which raised $19.8 billion globally in 2022.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge that 82% of companies that failed in 2023 did so because of cash flow issues, highlighting the importance of financial stability that collective funding can assist in achieving. The challenges faced by venture-backed U.S. real estate companies, which have seen an average decline of 85% from their offering price, illustrate the volatility present in the market. Yet, the strong enthusiasm from capital providers in the proptech sector indicates the strategic benefits of collective funding.
As the landscape of startup financing evolves, syndicate investment continues to emerge as a crucial element of the funding strategy, aligning with the growing trend of collaboration among investors at fff. Club. The procedure at fff. Club is intended to be seamless and user-friendly, ensuring that all individuals can engage effectively in these profitable opportunities.
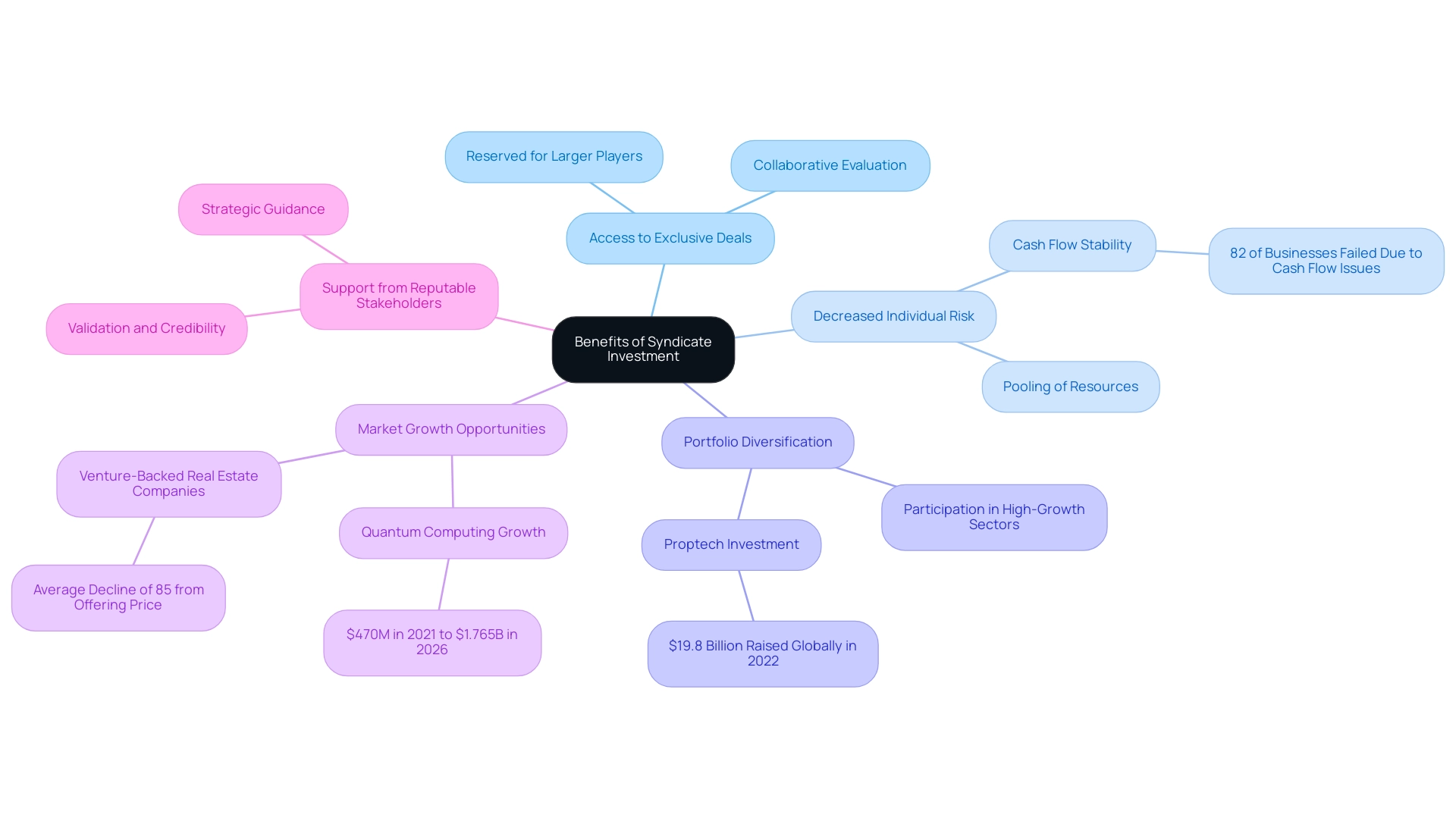
How to Form and Manage a Syndicate
Creating and overseeing a funding group necessitates a sequence of systematic actions that guarantee cohesion and efficiency among participants. At first, possible group members should concur on a common funding thesis or focus area, such as technology or healthcare startups. This foundational step helps streamline decision-making and resource allocation strategies.
Significantly, syndicate investment groups enable individuals to engage in screened financial opportunities in venture capital, private equity, real estate, and private credit with reduced funding minimums compared to direct placements, making it an appealing choice for technology stakeholders. Platforms like fff. Club offer access to these vetted opportunities, fostering a community-driven approach to investment.
Following this, the lead backer must define the structure of the syndicate investment, outlining the processes for decision-making and profit distribution. As Jenny Tooth, Executive Chair of the UK Business Angels Association, observes, 'We’ve stopped being in isolation in our investing, and we have welcomed international participants,' emphasizing the shift towards collaborative investing. This community-driven approach is further reinforced by platforms like fff.club, which engages over 400 tech investors in syndicate investment for collaborative wealth management.
Maintaining effective communication and openness is crucial; it cultivates trust and alignment among participants. Furthermore, due diligence on potential assets is crucial and should leverage the collective expertise of all members to evaluate opportunities comprehensively. A case study titled 'Advantages of Leading a Coalition' demonstrates that guiding a coalition can greatly enhance potential returns, as coalition leaders can utilize their network to secure larger funding through syndicate investment alongside their own.
For example, the case analysis emphasized a group that attained a 30% greater return on capital compared to conventional individual investing techniques. Frequent gatherings and updates are vital activities that keep all participants informed and actively involved throughout the syndicate investment process, ultimately enhancing the syndicate's likelihood of success. Furthermore, co-investing opportunities enable participants to combine resources, lowering personal risk while enhancing financial potential.
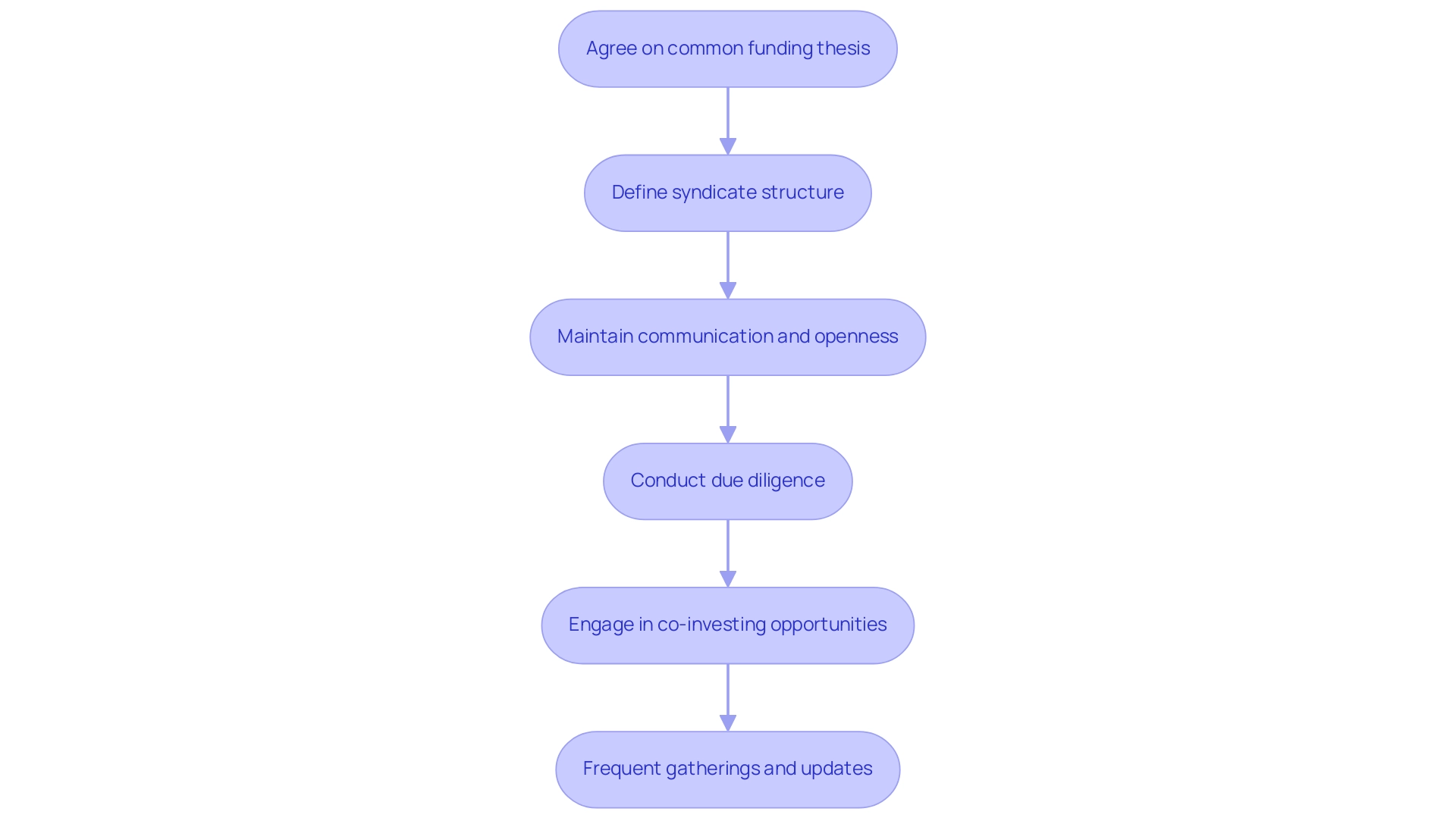
Understanding the Risks of Syndicate Investment
Syndicate investment can indeed yield significant rewards, particularly within the realms of venture capital, private credit, and real estate, but it is accompanied by considerable risks, especially given the volatile nature of startups. A stark illustration of the potential for loss is found in the staggering statistic that approximately 90% of startups ultimately fail, underscoring the need for careful consideration when engaging with private market opportunities. Moreover, groups frequently struggle with decision-making difficulties when individuals possess differing views on financial strategies, which can impede prompt actions.
The issue of illiquidity presents another risk; funds are typically committed for extended periods, often until a successful exit event materializes.
To effectively reduce these risks, participants must prioritize thorough due diligence, which involves examining the startups' business models and financial health. Defining clear criteria for financial contributions is essential for aligning expectations of participants and optimizing decision-making processes. Open communication throughout the funding lifecycle is equally important, fostering transparency and reducing misunderstandings among syndicate members.
As Sam Waldon, Acting Deputy Director of the Division of Enforcement, noted, 'The varied enforcement actions recommended by the Division in fiscal year 2024 demonstrate the Division keeping pace with emerging threats presented by misstatements regarding artificial intelligence... while maintaining its focus on ongoing risks such as material misstatements and major gatekeeper failures.' This highlights the necessity for vigilance in financial practices within the private market. Notably, the ongoing evolution of fraud tactics—such as the alarming case where a Hong Kong employee lost nearly $26 million to deepfake technology—highlights the risks individuals face today.
By learning from previous setbacks, such as the insider trading case involving Panuwat, where the SEC accused him of using confidential information to trade shares prior to a significant acquisition announcement, investors can strengthen their strategies for syndicate investment to navigate the complexities of collective funding more effectively.
Additionally, syndicate investment opportunities offer a valuable path for participants to collaborate and share insights, enhancing their collective investment strategies. Founders Akim Arhipov and Tim Vaino play pivotal roles in fostering these connections and guiding members through the intricacies of deal flow and due diligence. The SEC's success in obtaining favorable verdicts in trials also emphasizes the significance of regulatory oversight in protecting stakeholders.
Furthermore, engaging with educational resources and community initiatives at fff. Club can empower tech investors, providing them with the knowledge and support necessary to thrive in the private market landscape.
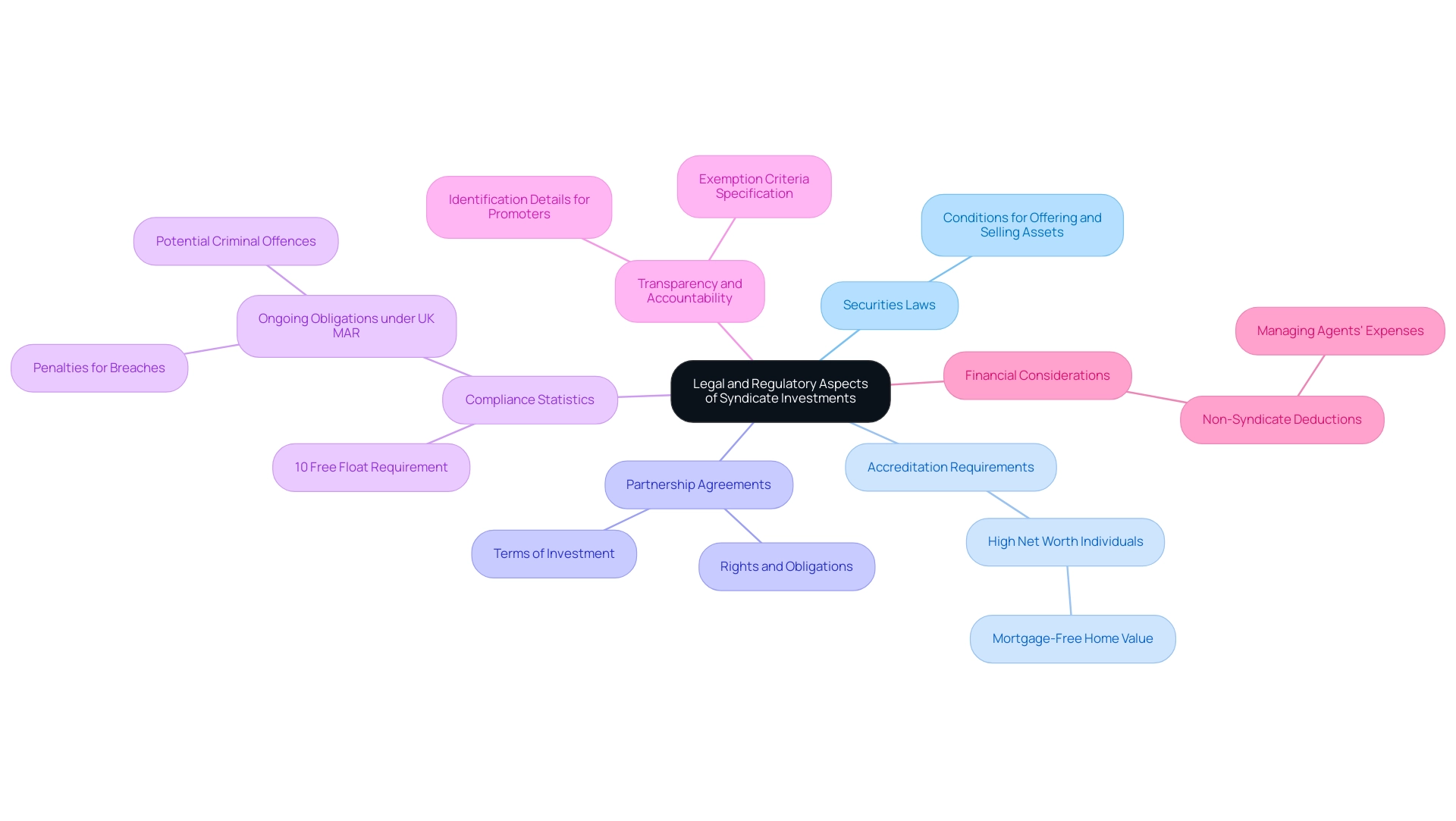
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Syndicate Investments
Syndicate funding is governed by a complex array of legal and regulatory frameworks that differ across jurisdictions. In general, these financial structures must adhere to securities laws that dictate the conditions for offering and selling assets. A critical aspect of this compliance involves verifying that all investors fulfill the necessary accreditation requirements, particularly since many groups cater to high-net-worth individuals.
Samantha Hayward, a Professional Trustee at Sestini & Co Pension Trustees, highlights the current relevance of these parameters, noting,
Absolutely. The current parameters have remained static for some time, meaning that there is a considerable portion of homeowners who are considered to be High Net Worth based on the value of their mortgage-free homes.
Furthermore, partnership agreements must meticulously delineate the terms of investment, alongside the rights and obligations of all members involved.
To navigate these complexities effectively, it is prudent for group leaders to seek counsel from legal professionals, ensuring adherence to all applicable laws while safeguarding the interests of each participant. Compliance statistics reveal that companies seeking admission to the Main Market must maintain at least a 10% free float, which is essential for understanding the financial health and adherence of groups. Furthermore, ongoing responsibilities under UK MAR emphasize that violations can lead to serious consequences, such as penalties and administrative measures, highlighting the legal risks connected to group financing.
Notably, recent updates necessitate that promoters of financial contributions provide identification details and specify exemption criteria, fostering greater transparency and accountability within the promotion framework. It’s also important to note that expenses incurred by managing agents cannot be allowed as separate non-syndicate deductions, which adds another layer of financial consideration for those involved in syndicate investment.
Conclusion
Syndicate investments represent a significant advancement in the landscape of funding for both investors and startups. By pooling resources, this collaborative model not only mitigates individual risks but also enhances access to exclusive opportunities that would otherwise be out of reach. The structured approach of syndicates, led by experienced investors, ensures thorough due diligence and strategic guidance, fostering an environment ripe for innovation and growth.
Investors benefit from the diversification of their portfolios while gaining insights from their peers, which ultimately leads to more informed decision-making. Startups, on the other hand, receive crucial capital and validation from credible backers, positioning them for success in competitive markets. The symbiotic relationship between investors and startups underscores the effectiveness of syndicate investments, particularly in dynamic sectors like technology and proptech.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential risks associated with syndicate investments. The high failure rate of startups and the challenges of decision-making within diverse groups necessitate a commitment to rigorous due diligence and clear communication among members. Legal and regulatory considerations further complicate the landscape, requiring careful navigation by syndicate leaders to ensure compliance and protect all participants.
As the trend of collaborative investing continues to gain traction, understanding the mechanics and intricacies of syndicate investments becomes essential for those looking to thrive in the evolving market. By embracing this model, both investors and startups can leverage the collective power of collaboration to drive growth and innovation, ultimately shaping the future of investment.



